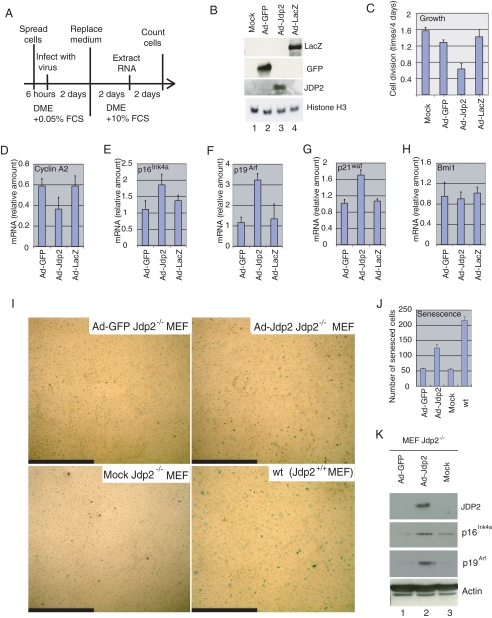
FIGURE 4.
JDP2 inhibits proliferation of MEF and promotes the expression of inhibitors of progression of the cell cycle. A, schematic diagram of the experiment. Fresh Jdp2-/- MEF were infected with Ad-GFP, Ad-Jdp2, or Ad-LacZ at an m.o.i. of 3 in the presence of DMEM plus 0.05% FCS. Two days after infection, the medium was replaced with DMEM plus 10% FCS, and the cells were harvested after further incubation for 2 days for extraction of RNA or for 4 days for quantification of cells. B, expression of GFP, JDP2, β-galactosidase (LacZ), and histone H3 in virus-infected cells. Extracts from 5 × 104 cells were analyzed by Western blotting with the relevant antibodies. C, effects of JDP2 on cell proliferation. Divisions per day of mock-, Ad-GFP-, Ad-Jdp2- and Ad-LacZ-infected cells are shown. D-H, expression of cyclin A2 (D), p16Ink4a (E), p19Arf (F), p21waf (G), and Bmi1 (H) was analyzed by real time RT-PCR with the appropriate primers. Levels of expression were normalized by reference to that of 18 S ribosomal RNA. I, induction of senescence by overexpression of JDP2. Jdp2-/- MEF, maintained in the presence of 3% O2, were infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-JDP2 at an m.o.i. of 3 and cultured in the presence of 20% O2 for 4 days. Then cells were subjected to senescence-associated staining of β-galactosidase. Mock-infected Jdp2-/- and WT MEF served as negative and positive controls, respectively. Scale bars, 1.0 mm. J, numbers of senescent cells. Senescent cells in a 6.2-mm2 field were counted, and results shown are the means ± S.E. of results from three independent experiments. K, expression of JDP2, p16Ink4a, p19Arf, and actin was examined in virus-infected cells. Extracts from 5 × 104 cells (20 μg of protein) were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies.