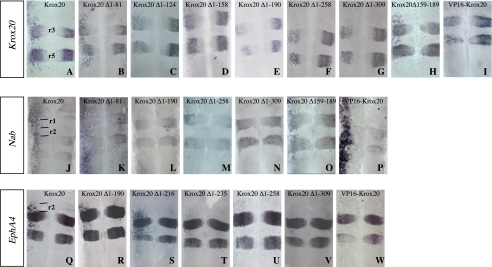
FIGURE 2.
The various Krox20 transcriptional activities are mediated by different domains. Chick embryo neural tubes were electroporated on the left side with wild type or truncated Krox20 expression constructs, as indicated, in situ hybridized with the probes indicated in the left panel, and flat mounted. The effects of the ectopic expression of the different constructs are determined by comparison of the in situ hybridization patterns observed in the left (experimental) and right (control) sides of the neural tube. A-I, analysis of endogenous Krox20 expression indicates in particular that deletion of the 190 N-terminal amino acids abolishes ectopic activation and even leads to repression of Krox20 in r3 and r5. J-P, Krox20 electroporation leads to ectopic activation of Nab with no rostral restriction, which is also lost upon deletion of the 190 N-terminal amino acids. Grafting of the VP16 acidic domain on an N-terminally deleted Krox20 restores the ability to activate Nab (P), but not Krox20 (I). Q-W, analysis of EphA4 expression indicates that ectopic activation is restricted to r2, r4, and r6 with a level decreasing rostro-caudally. Deletion of the 235 N-terminal amino acids eliminates most of this activity. Anterior is up. r, rhombomere.