FIGURE 7.
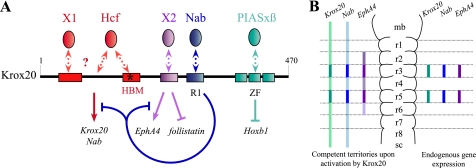
Schematic representation of Krox20 functional organization and of its competence territories in the hindbrain. A, several distinct domains are involved in the different Krox20 transcriptional activities and constitute established or putative binding sites for co-factors. The N-terminal part of the protein, which contains two acidic regions (red boxes), interacts with HCF-1, and at least another unknown cofactor (X1) is required for Krox20 and Nab activation. A domain located between positions 216 and 235 (purple box) is required for EphA4 activation and follistatin repression and may bind one or several unknown factors (X2). The previously described R1 domain (blue box) binds Nab factors that antagonize Krox20 activation functions and establish a negative feedback loop. The zinc finger (ZF) DNA binding domain is sufficient for Hoxb1 repression via the interaction with PIASxβ. B, endogenous Krox20, Nab, and EphA4 expression is restricted to r3 and r5 (right). Upon exogenous Krox20 expression, ectopic activation of the three targets is observed (left) with distinct territories of competence; Krox20 and Nab expression shows no restriction, and EphA4 expression is confined to the r2-r4-r6 region with a decreasing rostro-caudal gradient. mb, midbrain; r, rhombomere; sc, spinal cord.