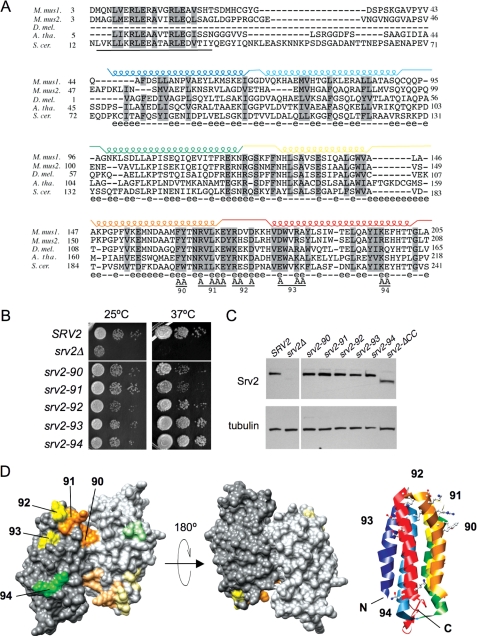
FIGURE 3.
Mutational analysis of the Srv2 HFD domain. A, alignment of N-terminal sequences for diverse Srv2/CAP homologues using ClustalW. M. mus1, mouse CAP1; M. mus2, mouse CAP2; D. mel., Drosophila melanogaster CAP; A. tha, Arabidopsis thaliana CAP; and S. cer., S. cerevisiae Srv2. Residues 73-241 in S. cerevisiae Srv2 form the HFD domain (18). Each helix is indicated above the primary sequence and color-coded. Solvent-exposed residues are designated below the primary sequence (e indicates solvent-exposed; - indicates for solvent-inaccessible). Below the alignment, the predicted coiled coil domain (residues 14-34) is underlined, and residues changed to alanine are marked A for each srv2 allele (numbered 90-94). B, SRV2 and srv2 mutant strains were grown to log phase, serially diluted, and plated on YPD plates at 25 and 37 °C to compare cell growth. C, immunoblot of whole cell extracts from SRV2 and srv2 mutant strains probed with anti-Srv2 antibodies and tubulin antibodies as a loading control. D, srv2 mutations modeled on a rendered view of the crystal structure of the dimeric, anti-parallel HFD from Dictyostelium Srv2/CAP (Protein Data Bank code 1S0P). Residues mutated in each allele are color-coded by the relative severity of their cell growth phenotype (orange, severe; yellow, mild; green, pseudo-wild type). Shading is lighter on one Srv2 molecule in the dimer. A ribbon structure is also shown for one molecule in the dimer, with helices color-coded to match those in A. The ribbon view has the same orientation as the rendered structure on the far left.