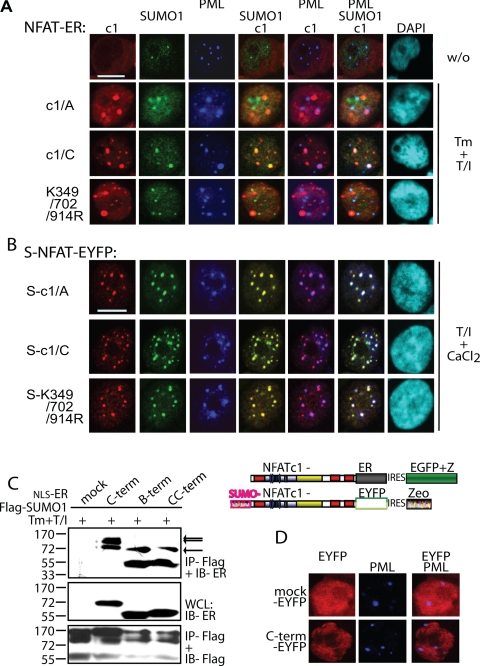
FIGURE 3.
Sumoylation directs NFATc1 into PML-nbs. A, the sumoylatable long isoform colocalizes with PML-nbs. Human A3.01 cells retrovirally infected with constructs expressing c1/A-, c1/C-, and K349R/K702R/K914R-ER and selected by zeocin were left untreated or stimulated (w/o) with Tm+T/I for 4 h. IF was performed with anti-ERα (to detect exogenous NFATc1), anti-SUMO1, and anti-PML followed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. B, the fusion with SUMO directs any NFATc1 isoform to PML-nbs. 293T HEK cells were transfected with SUMO(S)-c1/A, -c1/C, and -K349R/K702R/K914R fused to EYFP at the C terminus and treated with T/I+CaCl2 for 1 h. IF with anti-SUMO1 and anti-PML was performed for triple localization analyzed by confocal microscopy. The scale bar represents 10 μm. C, the C-terminal peptide is sumoylated. 293T HEK cells were transfected with FLAG-SUMO1 and C terminus-specific peptides fused to ER with the addition of an nuclear localization signal. Analyzes were performed as for Fig. 1F. WCL, whole cell lysates. D, the sumoylated C terminus is not sufficient for recruitment to PML-nbs. Procedures were as in A but after infection of A3.01 with a retroviral vector expressing the C terminus-specific peptide fused to EYFP. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; IRES, internal ribosome entry site.