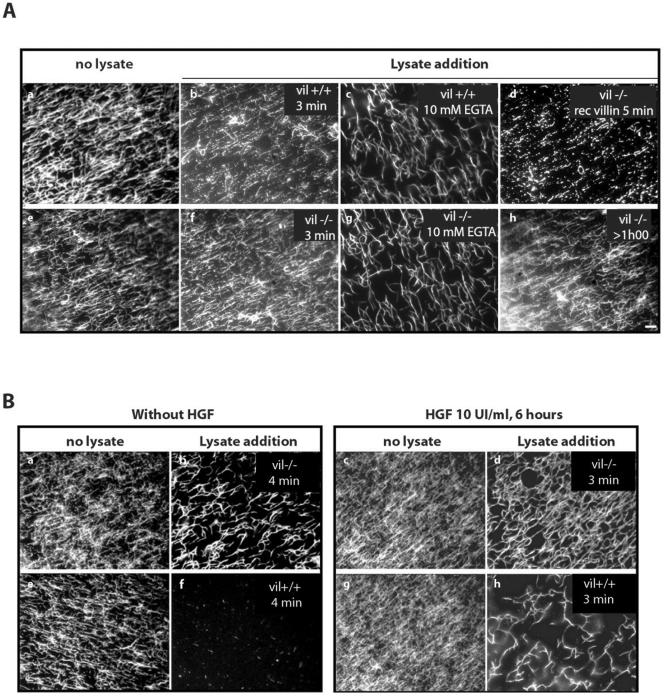
Figure 3.
Villin induces F-actin reorganization in vitro. Rhodamine-labeled actin filaments were prepared as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. They were allowed to attach to a nitrocellulose matrix on a glass coverslip mounted as a flow chamber during 15 min on ice. After washing with an antibleaching buffer, 12 μl of cell lysate (10 mg/ml) was perfused and the analysis was directly performed under fluorescent microscopy. (A) Enterocyte lysates. a and e, rhodamine-labeled F-actin filaments before lysate perfusion as internal controls. Note that in absence of any perfusion, the actin filaments correspond to disorganized actin network. B, 3 min after vil+/+ lysate addition. c, 5 min after EGTA treated vil+/+ lysate addition. f, 3 min after vil-/- lysate addition. g, 5 min after EGTA-treated vil-/- lysate addition. d, perfusion of vil-/- lysate followed by addition of 1 μg/μl recombinant villin during 5 min. h, actin filaments >1 h after vil-/- lysate perfusion. (B) MDCK cells lysates. a, c, e, and g, actin filaments before lysate perfusion. In absence of HGF, vil-/- (b) and vil+/+ (f) lysates. After 6 h of HGF stimulation, vil-/- (d) and vil+/+ (h) lysates. Bar, 10 μm.