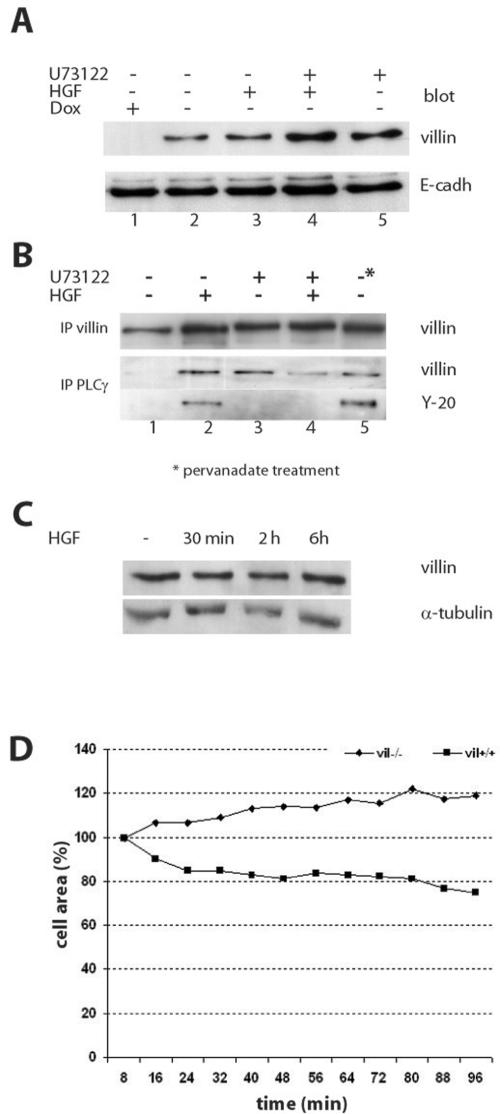
Figure 8.
HGF stimulation induces villin association to the plasma membrane and increases its association to PLCg. (A) Villin redistribution in the membrane fraction upon HGF stimulation. This figure presents villin and E-cadherin blotting, shown as a control for equal loading. Cells were either unstimulated (lane 2), stimulated with HGF for 2 h (lane 3), treated with U73122 (10 μM) to inhibit PLCγ (lane 5), or double-treated with HGF and U73122 (lane 4). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of villin and PLCγ in the membrane fraction. The first panel presents villin immunoprecipitation, blotted for villin. The second panel presents PLCγ immunoprecipitation blotted either for villin or for tyrosine phosphorylated proteins. The tyrosine-phosphorylated protein detected was at the molecular weight of villin. For all panels, the lanes are the following: lane 1, unstimulated cells; lane 2, after 2 h of HGF stimulation; lane 3, after U73122 (10 μM) treatment, lane 4, double treated with HGF and U73122; and lane 5, unstimulated cells but treated with pervanadate to induce protein phosphorylation. (C) Villin and α-tubulin blotting in total cell lysates before and after HGF treatment. (D) Lamellipod extension assays in presence of HGF in vil-/- and vil+/+ cells pretreated with U73122 (10 μM). Data are represented as the percentage of the initial cell area (T0).