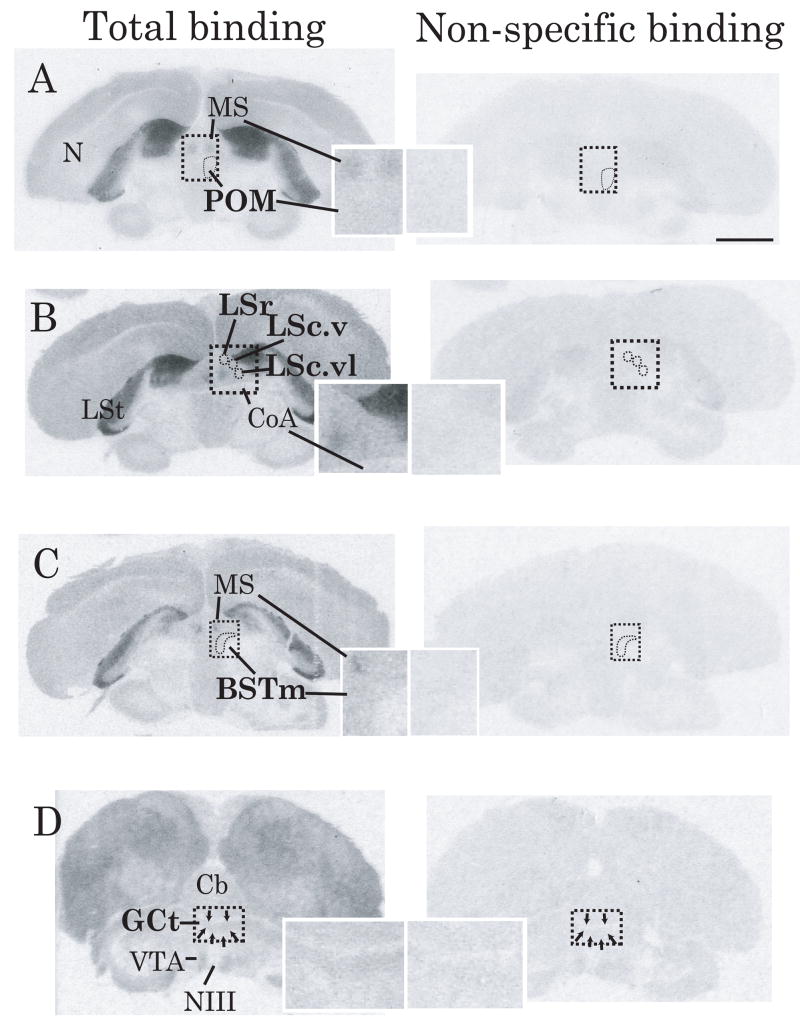
Figure 1.
A) Representative autoradiograms illustrating differences between total (left column) and non-specific (right column) D1-like receptor binding in sections containing regions in which binding related to song; A) POM, B) Subdivisions of LS, C) BSTm, and D) GCt. The boundaries of POM, subdivisions of LS, BSTm and GCt are indicated within the dashed boxes. Overlays contain magnified images (500%) of the area blocked off in the images at lower magnification. In all brain regions examined in all animals, total binding was higher than non-specific binding. Thus, to determine specific binding, non-specific binding values were subtracted from total binding values. Abbreviations: N = nidopallium, MS = medial septum, LSt = lateral striatum, CoA = anterior commissure, Cb = cerebellum, NIII = 3rd cranial nerve. See text for additional abbreviations. Contrast was adjusted identically using Adobe Photoshop Elements 6.0 for all images. Scale bar in top right figure = approximately 3 mm.