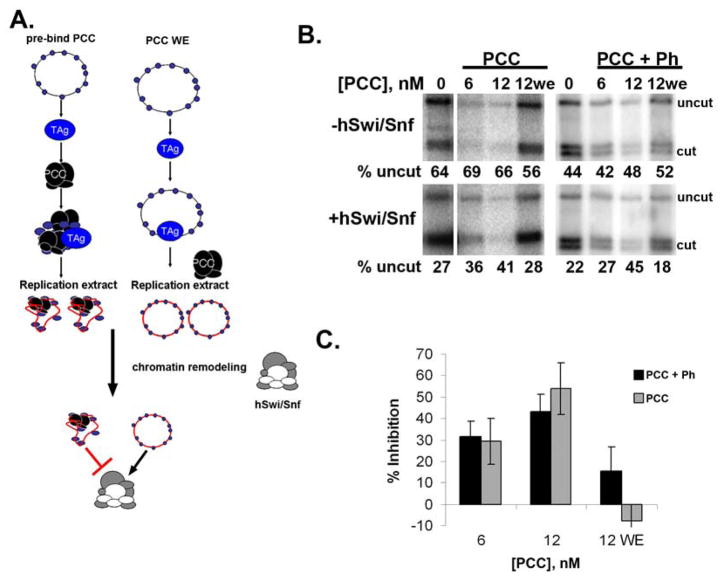
Figure 1. PCC inhibits chromatin remodeling of replicated templates.
A. Reaction scheme for in vitro replication followed by chromatin remodeling. The scheme on the right is the control in which PCC is added with the replication extract (WE). B. Example of restriction enzyme accessibility assay carried out after in vitro replication of chromatin. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling by hSwi/Snf decreases the fraction of the template that is uncut (compare top and bottom panels); this reaction is inhibited when PCC is bound to chromatin prior to in vitro replication. Panel shows phosphorimager scan of chromatin remodeling reactions so that only replicated templates (that incorporated radiolabeled dATP during replication) are visible. PCC+Ph contains PSC, Pc, dRING, and Ph, while PCC has only PSC, Pc, dRING (see sFig. 1E). C. Summary of inhibition of chromatin remodeling of replicated templates. Error bars in all Figures are SEM unless otherwise indicated.