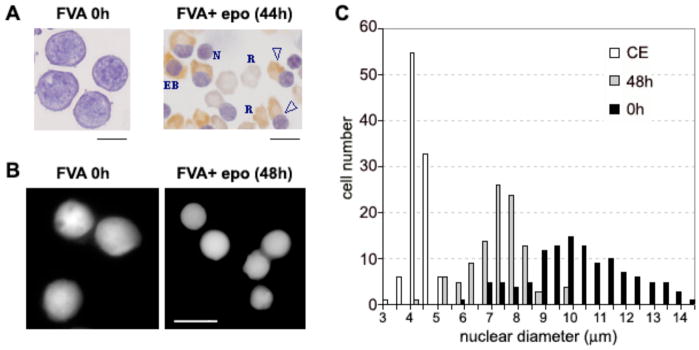
Fig. 1.
Nuclear condensation and extrusion during terminal differentiation of murine erythroblasts in the FVA model system. (A) Bright field micrograph of cytospin preparations at 0 h and 44 h. EB, late erythroblast; open triangle, enucleating erythroblast; R, reticulocyte; N, expelled nucleus. (B) Fluorescence microscopy of 0 and 48 h fixed cells stained with Hoechst 33258 for DNA. (C) Histogram showing nuclear diameter distribution in terminally differentiating murine erythroblasts at 0 h (black bars) and 48 h (gray bars) compared with chicken erythrocytes (open bars). Nuclear diameter measurements were performed by fluorescence microscopy on fixed cells stained with Hoechst 33258 for DNA. Scale bars, 10 μm.