Figure 3.
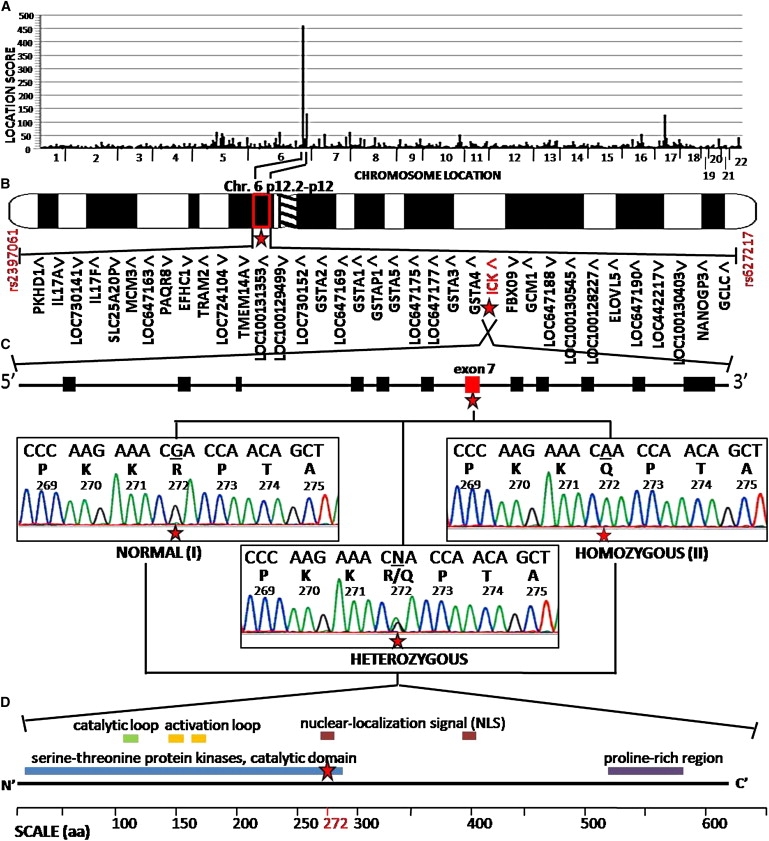
Autozygosity Mapping of ECO-Affected Pedigree Identified an Amino Acid Change, R272Q, in ICK
(A) Autozygosity mapping with SNP genotypes from 500,000 SNP microarrays across the chromosomes (x axis) yielded SNP haplotype location scores (y axis), with the highest peak on chromosome 6. Location score is the summation of the point LOD scores representing the likelihood of observing contiguous homozygosity in all five affected individuals of each SNP within the region of homozygosity.13
(B) Expanded view of the candidate locus shows the peak to be on chromosome 6p12.2–p12 (indicated by a star), which is defined by SNPs rs2397061 and rs627217 and consists of 36 candidate genes, including ICK (indicated in red with a star), distributed over 1.8 Mb of the genome. Transcriptional direction is indicated by arrowheads.
(C) The genomic structure of ICK gene consists of 12 coding exons with a nonsynonymous nucleotide change in exon 7 (indicated in red with a star) that alters the amino acid of arginine to glutamine at residue 272 (R272Q). DNA sequence analysis of ICK exon 7 from genomic DNA of a normal (I, top left tracing) individual, an affected (II, top right tracing) individual, and a R272Q heterozygote (bottom middle tracing). For each tracing, a normal nucleotide sequence is shown in the top line of letters, with single-letter amino acid codes and codon numbers beneath. The position of the mutated nucleotides is indicated by the star.
(D) The domain structure of ICK protein consists of the protein serine-threonine kinase catalytic domain, a catalytic loop, two activation loops, two nuclear-localization-signal sites, and a proline-rich region, from the N-terminal to C-terminal end. The amino acid (aa) 272 (indicated in red) lies within the nuclear-localization signal (indicated with a star).
