Figure 4.
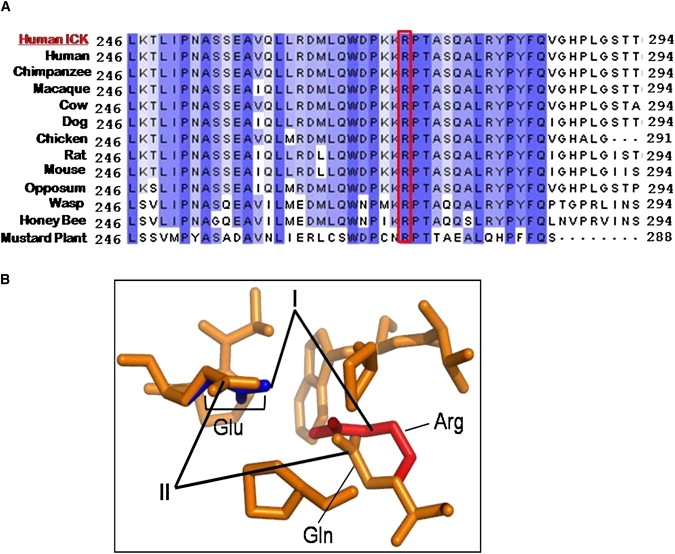
ICK Protein Analysis Demonstrates that R272 Is Highly Conserved and that the R272Q Mutation Alters Protein Structure
(A) Multiple alignments demonstrate that R272 residue is highly conserved across a representative set of species-specific ICK homologs. A ClustalW analysis of the ICK region encompassing the mutation site at residue 272 (highlighted in red) in aligned homologs with multiple divergent sequences is shown. The residues shaded in blue indicate amino acids that are similar between homologs.
(B) A magnified look at the 3D region surrounding residue 272 in ICK according to PyMOL modeling, such that the normal (I) protein is superimposed on the R272Q mutant (II) protein. This modeling predicts that the arginine (Arg, in red) and glutamic acid (Glu, in blue) form an ionic pair because of close proximity, in normal or wild-type protein (indicated by I). By comparison, the R272Q mutant (indicated by II) is a basic polar to neutral polar substitution and predicts a change in structure such that the glutamine (Gln, in orange) and glutamic acid (Glu, in orange) can no longer ion pair, leaving the glutamic acid exposed to the surface of the protein rather than buried within the 3D structure.
