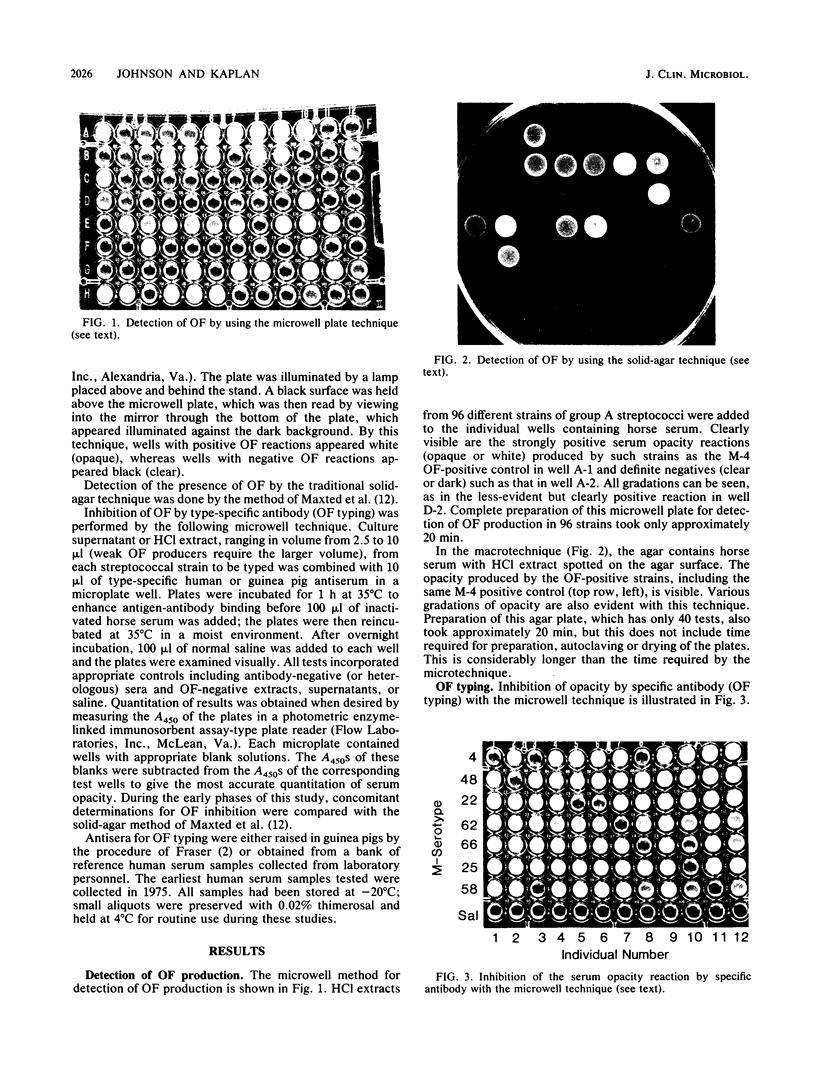
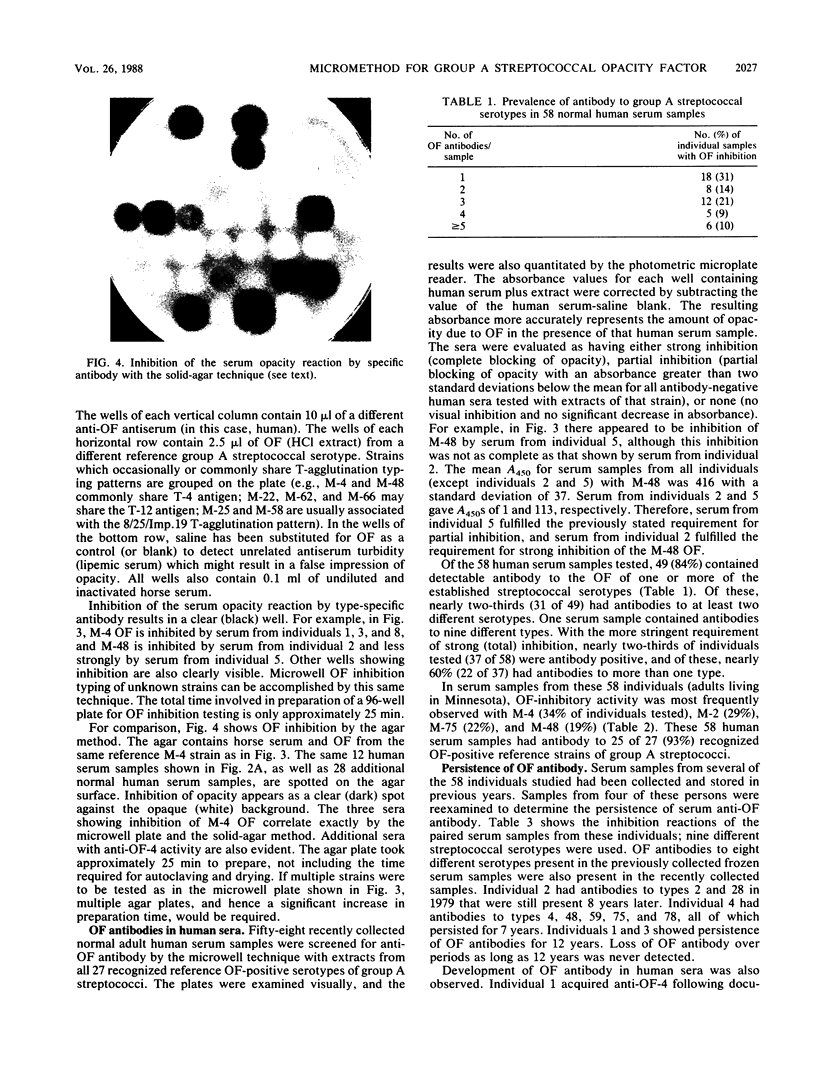
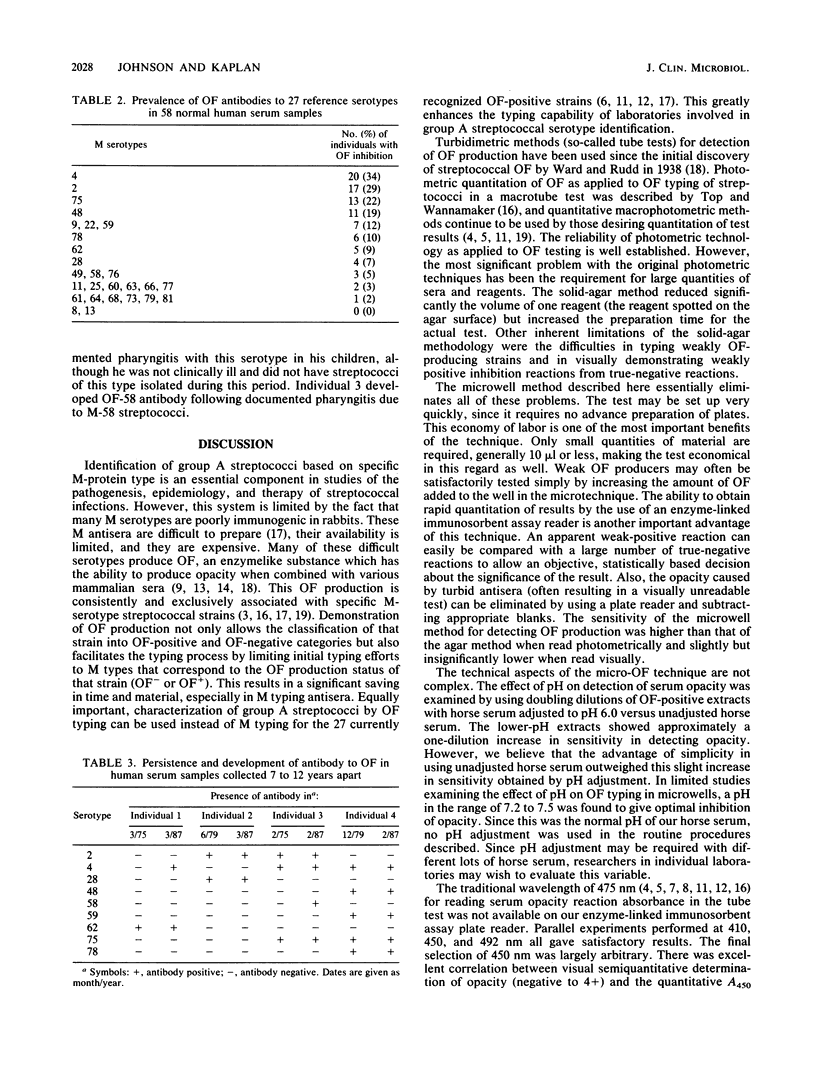
Abstract
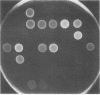
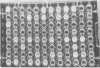
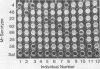
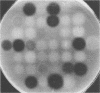
We have developed a microtechnique for detection of streptococcal serum opacity factor (OF) and for typing of group A streptococci by inhibition of OF. This technique, which involves the use of single wells of standard 96-well tissue culture plates, offers several advantages over previous methods: no advance test preparation is required, allowing tests to be quickly and easily performed; only small quantities of reagents are required; results can be determined visually (qualitative) or by using a photometric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay plate reader (quantitative); and human serum samples may be quickly and easily screened for OF-inhibitory antibody and subsequently used in place of difficult-to-produce and expensive hyperimmune animal sera for OF characterization of group A streptococci. Fifty-eight samples of normal adult human serum were tested by this new microtechnique for anti-OF antibodies, and 49 (84%) were found to have antibody against 1 or more of the 27 recognized OF-positive serotypes. OF antibodies to M-4, M-2, M-75, and M-48 were most common in these individuals. These 58 human serum samples collectively contained antibody to 25 of the 27 different OF-producing serotypes. Serum samples from four individuals were tested for persistence of OF antibody. OF antibodies to eight different serotypes present in the serum samples collected 7 to 12 years previously were present in the freshly collected sera, indicating that OF antibody persists in human antisera for many years. This new technique has distinct advantages and makes it possible for many laboratories to use this technique to characterize group A streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fraser C. A. Preparation of specific antisera to the opacity factors of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1982 May;15(2):153–162. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-2-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODER H. Association of a serum opacity reaction with serological type in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jul;25:347–352. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallas G., Widdowson J. P. The opacity factor of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):451–464. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallas G., Widdowson J. P. The relationship between opacity factor and M protein in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Feb;16(1):13–26. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iontova I. M., Totolian A. A. Lipoproteinase of group A streptococci and the antibodies in human sera. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Dec;233(4):452–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iontova I. M., Totolian A. A. Serologicheskie svoistva streptokokkovykh lipoproteinaz. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):36–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUMWIEDE E. Studies on a lipoproteinase of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1954 Dec 1;100(6):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.6.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Persistence of type-specific antibodies in man following infection with group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Aug 1;110(2):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Widdowson J. P., Fraser C. A. Antibody to streptococcal opacity factor in human sera. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):35–42. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Widdowson J. P., Fraser C. A., Ball L. C., Bassett D. C. The use of the serum opacity reaction in the typing of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):83–90. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWEN R., MARTIN J. ENHANCEMENT OF CHOLESTEROL ESTERIFICATION IN SERUM BY AN EXTRACT OF GROUP-A STREPTOCOCCUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:396–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWEN R. The release of cholesterol esters from serum lipoproteins by extracts of certain group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:807–823. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes. The demonstration of multiple, strain-specific lipoproteinase antigens. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):1013–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes: frequency of production of streptococcal lipoproteinase by strains of different serological types and the relationship of M protein production. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Mar;66(1):49–58. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L. The production of opacity in serum by group A streptococci and its relationship withthe presence of M antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):343–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]