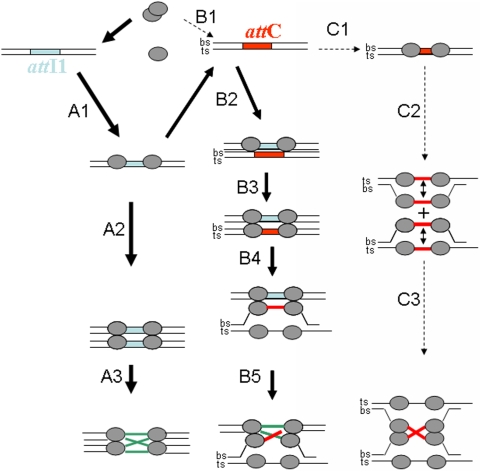
Figure 5. Model for the cooperative binding and the inti1 oligomers involved in the in vitro recombination catalyzed by IntI1.
In the attI1×attI1 recombination reaction IntI1 binds both dsattI1 fragment as a dimer and catalyzes the strand exchange and the formation of the HJ intermediate (lanes A1 to A3). In the case of attI1×attC recombination, IntI1 binds dsattC only slightly (B1). Interaction with the first attI1 substrate led to cooperative binding to the second attC site (B2), allowing the recruitment of a second IntI1 dimer on the second strand of the attC site (B3) and the formation of the tetrameric intermediate, leading in turn to the stabilization of a ssattC intermediate (B4). The strand exchange between dsattI1 and bsattC can then be catalyzed (B5). Recombination activity detected in presence of two attC sites suggests that the initial low binding of the enzyme to this site is sufficient for triggering all the subsequent recombination steps (way C). ts: top strand, bs: bottom strand.