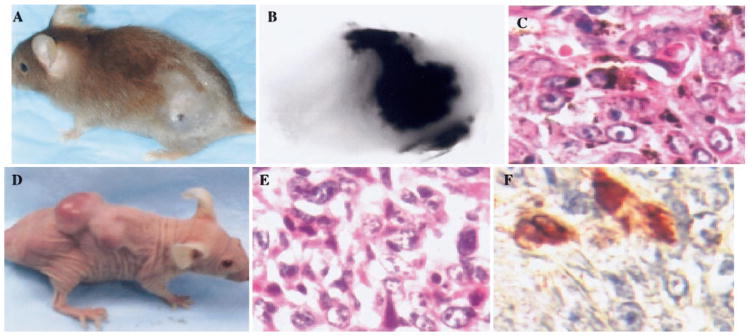
Fig. 4.
Histological analysis of melanoma lesions that developed in association with overexpression of MIP-2 and loss of p16. (A) Typical cutaneous-pigmented melanoma lesion arising pigmented melanoma lesion arising in MIP-2-transgenic mice heterozygous for INK4a/ARF. (B) Morphology of the melanoma. (C) H&E staining of tissue section from a typical pigmented melanoma arising in MIP-2 transgenic mice. Melanoma formation in nude mice transplanted with MIP-2-transgenic melanocytes that were null for INK4a/ARF. Two million epidermal melanocytes derived from MIP-2-transgenic, newborn mouse completely deficient for INK4a/ARF were injected in the subscapular region of nude mice. (D) After 101 days of latency, skin melanoma lesions were observed. (E) H&E staining reveals the histological characteristics of a melanocytic tumor lesion. S-100 immunostaining of tumor cells in lung. (Photocopied with permission from ref. [117].)