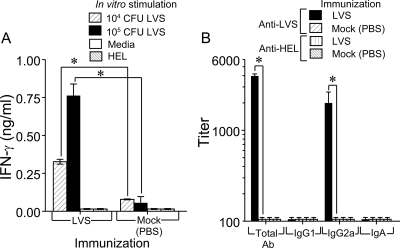
FIG. 2.
Oral LVS vaccination induces LVS-specific IFN-γ and serum antibodies. (A) Groups of BALB/c mice (n = 5) were either vaccinated orally with 103 CFU of LVS or mock immunized with PBS. Spleens were removed 14 days later, and single cells were prepared and incubated for 72 h in the presence of UV-inactivated LVS at two doses (104 and 105), medium alone, or the unrelated antigen HEL. Supernatants were analyzed for IFN-γ production. *, differences in IFN-γ production between LVS- and mock-immunized (PBS) mice were significant at a P value of <0.001 (statistical power, 1 with an alpha of 0.50). (B) Groups of BALB/c mice (n = 8) were immunized orally with 103 CFU of LVS in PBS and were rested for 21 days. Blood was collected, and prepared sera were analyzed by isotype-specific ELISAs using microtiter plates coated with UV-inactivated LVS. The results are reported as 50% end point titers. *, differences in antibody titers between immune and nonimmune sera were significant at a P value of <0.001 for total antibody (Ab) (statistical power, 1 with an alpha of 0.50) and at a P value of 0.015 for IgG2a (statistical power, 0.767 with an alpha of 0.50). Results are representative of two separate experiments.