FIG. 8.
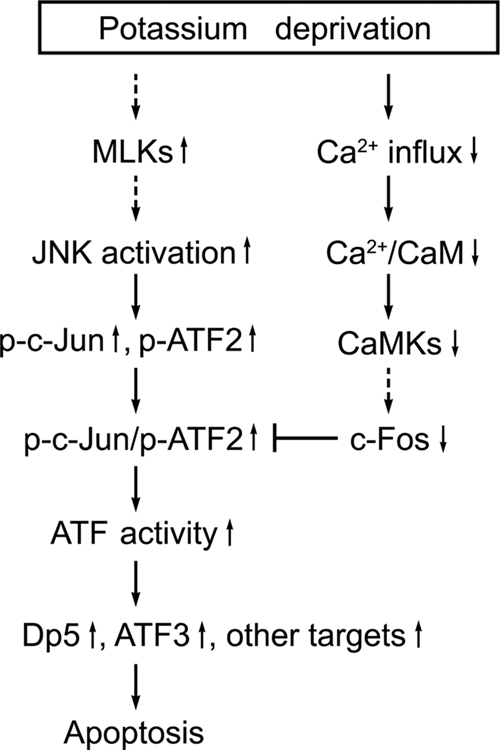
Model for the signaling pathways regulating potassium deprivation-induced CGN apoptosis. Deprivation of the survival agent, potassium, not only results in JNK-dependent transactivation of c-Jun and ATF2 via phosphorylation of their N-terminal regions but also leads to concurrent c-Fos downregulation attributable to the decreased activity of Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM) and CaMKs secondary to a loss of calcium influx. c-Jun primarily heterodimerizes with ATF2, and c-Jun/ATF2 heterodimers are responsible for the upregulation of ATF activity. c-Fos downregulation facilitates the heterodimerization between c-Jun and ATF2. The upregulation of ATF activity triggers target gene expression (dp5, atf3, and other genes) to promote neuronal apoptosis. p-c-Jun, phospho-c-Jun.
