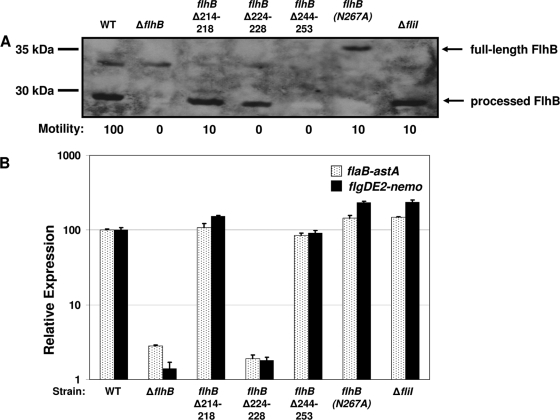
FIG. 5.
Phenotypic analyses of C. jejuni strains with formed but secretion-impaired FEA complexes. (A) Immunoblot analysis of FlhB proteins and motility phenotypes of C. jejuni wild-type and flhB or fliI mutant strains. Total membrane proteins were isolated from wild-type and mutant strains of C. jejuni. Equal amounts of proteins from the strains were analyzed. Anti-FlhB Rab476 antiserum was used to detect the FlhB proteins. The arrows indicate the positions of the 37-kDa full-length, unprocessed FlhB protein and the 30-kDa processed FlhB protein. The motility phenotypes of wild-type and mutant strains are indicated below the blot. The diameter of the motile ring around the point of inoculation in MH semisolid agar was measured after 36 h of incubation at 37°C under microaerobic conditions. The level of motility of each mutants is expressed relative to the level of motility of the wild-type strain, which was defined as 100%. The strains used for both analyses included (from left to right) wild-type strain DRH461 (WT), DRH1734, SNJ464, SNJ428, SNJ475, and SNJ438. (B) Arylsulfatase assays for analysis of expression of flaB::astA and flgDE2::nemo in C. jejuni 81-176 Smr wild-type or mutant strains containing a secretion-impaired FEA. The results are the results of a typical assay in which each strain was tested in triplicate. The values reported for each strain are the average arylsulfatase activity ± standard deviation relative to the level of expression of each transcriptional fusion in wild-type strain 81-176 Smr ΔastA, which was defined as 100 arylsulfatase units. For expression of flaB::astA, the strains used included (from left to right) wild-type strain DRH665 (WT), DRH1830, SNJ467, SNJ434, SNJ508, SNJ442, and SNJ422. For expression of flgDE2::nemo, the strains used included wild-type strain DRH533 (WT), DRH1827, SNJ466, SNJ433, SNJ504, SNJ439, and SNJ457. The type of mutation in the FEA of each strain is indicated below the graph.