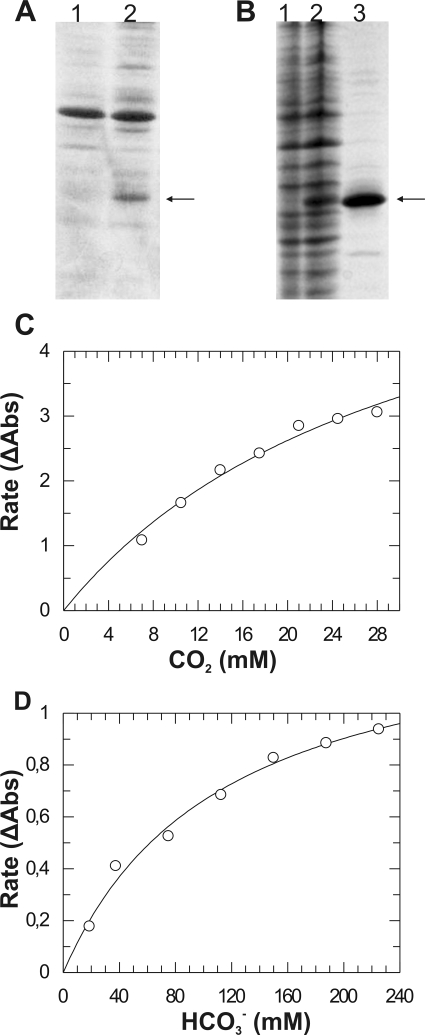
FIG. 2.
Heterologous expression, purification, and enzymatic assays for CA activity of the recombinant CAA1 polypeptide. (A) Accumulation of the recombinant CAA1+ polypeptide (arrow) containing the predicted N-terminal signal peptide in the E. coli periplasmic proteins (lane 2) in comparison to periplasmic proteins from E. coli cells transformed with the empty vector (lane 1). (B) Expression and purification of the recombinant CAA1− polypeptide (arrow) lacking the N-terminal signal peptide. Lane 1, total soluble proteins from E. coli cells transformed with the empty vector; lane 2, total soluble proteins from E. coli cells transformed with the CAA1− expression plasmid; lane 3, purified CAA1− recombinant polypeptide. (C) Kinetic analysis of the CO2 hydration activity was performed at pH 7.5 in HEPES/NaOH buffer. (D) Kinetic analysis of the bicarbonate dehydration activity was performed at pH 6.3 in MES/KOH buffer. Kinetic parameters were calculated by fitting the corrected rate data (change in absorbance per min [ΔAbs]) to the Michaelis-Menten equation using the program GraFit v3.5. The rates shown are means of three repeats (n = 3).