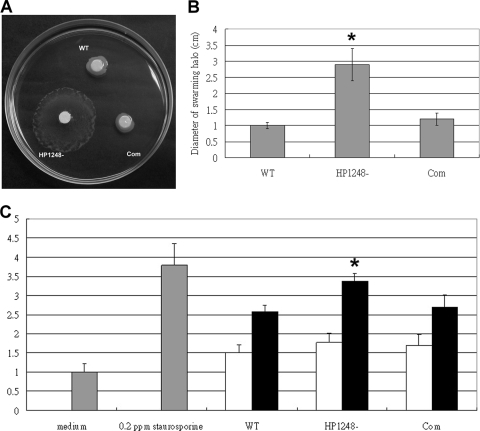
FIG. 4.
H. pylori strain lacking HP1248 is more motile and induces more macrophage apoptosis. (A) The C1/HP1248-cat mutant strain formed a larger swarming halo than the wild-type and complementation strains. The photograph shows a Brucella broth-10% FBS soft agar plate after 4 days of incubation. WT, HP1248−, and Com indicate the wild type, C1/HP1248-cat mutant strain, and HP1248 complementation strain, respectively. (B) Quantitative analysis of the diameter of the swarming halo (cm). Values are expressed as means ± standard deviations for experiments performed in triplicate. The HP1248− mutant strain formed a larger swarming halo than the wild type (*, P < 0.01, Student's unpaired t test). (C) RAW 264.7 cells infected with H. pylori at an MOI of 50:1 (black bars) or 30:1 (white bars). RAW 264.7 cells infected with H. pylori wild-type NTUH-C1 (WT) showed an increase in apoptosis in comparison with results for uninfected controls (medium). However, the C1/HP1248-cat deletion mutant strain (HP1248−) showed an increase in apoptosis compared to results for RAW 264.7 cells infected with the wild-type strain at an MOI of 50:1 (*, P = 0.0107, Student's unpaired t test). The relative apoptosis level of HP1248− is 3.37 ± 0.21 at an MOI of 50:1 and 1.77 ± 0.25 at an MOI of 30:1. Complementation of HP1248− (Com) can decrease the ability to induce apoptosis to the WT level. Macrophage apoptosis levels were assessed by ELISA. The OD of unstimulated control cells (medium only) was assigned a value of 1.0, and the relative amounts of apoptosis in experimental groups were determined as ratios to the control level. Values are expressed as means ± standard deviations for experiments performed in triplicate. Staurosporine (0.2 ppm) was used as a positive control.