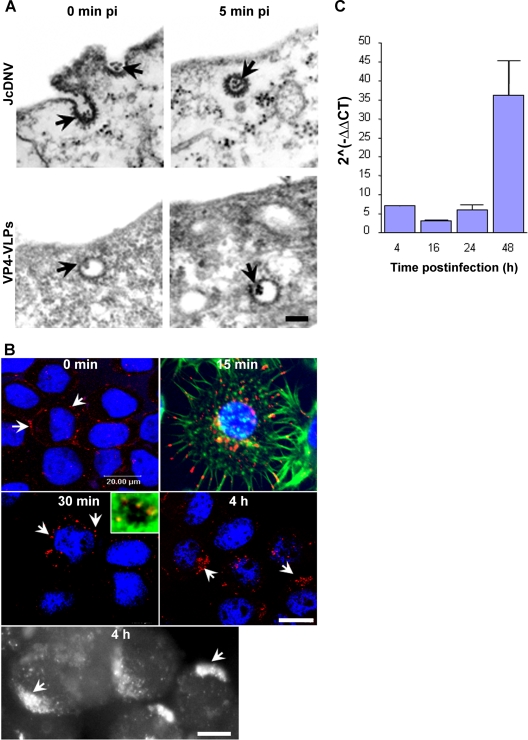
FIG. 1.
Uptake and kinetics of JcDNV internalization and DNA replication within L. dispar cells. (A) Electron microscopy analysis of JcDNV (upper) and VP4-VLPs (lower) entry into L. dispar 652 cells. L. dispar cells were incubated with JcDNV virus particles or VP4-VLPs at 4°C for 1 h and then shifted to 28°C for 0 or 5 min before fixation and preparation for TEM examination. Scale bar, 100 nm. The arrows indicate either JcDNV or VLP4-VLPs. (B) Kinetics of JcDNV internalization within L. dispar cells was analyzed by immunofluorescence at various times p.i. L. dispar cells were infected with JcDNV as specified in Materials and Methods and immunolabeled with anti-JcDNV antibody (red). Confocal optical sections and epifluorescence images (black and white) of infected cells were examined at 0 min, 15 min, 30 min, and 4 h p.i. Arrows indicate JcDNV immunostaining. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. The inset is a confocal optical section of JcDNV-infected cells at 30 min p.i. Actin was labeled with phalloidin (green), and the nucleus was labeled with DAPI (blue). (C) JcDNV DNA replication kinetics. L. dispar cells were infected with JcDNV (0.1 TCID50 unit per cell) for 1h at 4°C, followed by washing to remove unbound virus, and were further incubated at 28°C. At various times p.i., total DNA was extracted and quantified with real-time PCR. Viral DNA was quantified using virus-specific primers, and the actin gene was used to quantify cellular DNA. Values represent the mean ratio of viral/cellular DNA of two different experiments.