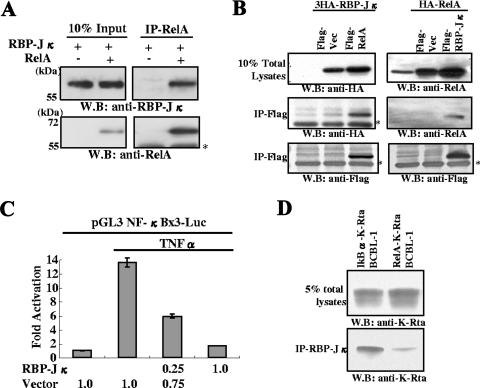
FIG. 6.
RBP-Jκ interactions with Rel-A and functional consequences. (A) Association between RelA and RBP-Jκ. Purified RelA (0.1 μg) and RBP-Jκ (0.1 μg) were mixed in binding buffer, incubated at 4°C, and immunoprecipitated with anti-RelA antibody. The immunoprecipitate was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisk shows the position of the IgG heavy chain. W.B., Western blot. (B) Association between RelA and RBP-Jκ in transfected 293T cells. The indicated plasmids were cotransfected into 293T cells. Total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with agarose beads conjugated with anti-Flag antibody. Immunoprecipitates were probed with the indicated antibodies. Endogenous RelA was also detected with anti-RelA rabbit IgG (right upper panel). (C) Suppression of NF-κB activation by RBP-Jκ. The NF-κB reporter was cotransfected with the RBP-Jκ expression plasmid. NF-κB was activated by treating the cultures with TNF-α at 24 h posttransfection. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were harvested, and levels of luciferase were determined. Fold activation over the control transfected value is shown. The amount of plasmid used is indicated at the bottom of the panel. (D) RelA expression reduced K-Rta binding to RBP-Jκ. Dual expression of IκBα and K-Rta or RelA and K-Rta was induced in BCBL-1 by adding doxycycline. After 12 h of induction, cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-RBP-Jκ antibody. Coimmunoprecipitated K-Rta was measured by immunoblotting with anti-K-Rta antibody. Due to similar molecular masses, the presence of rabbit IgG heavy chain obscured the detection of the immunoprecipitated RBP-Jκ.