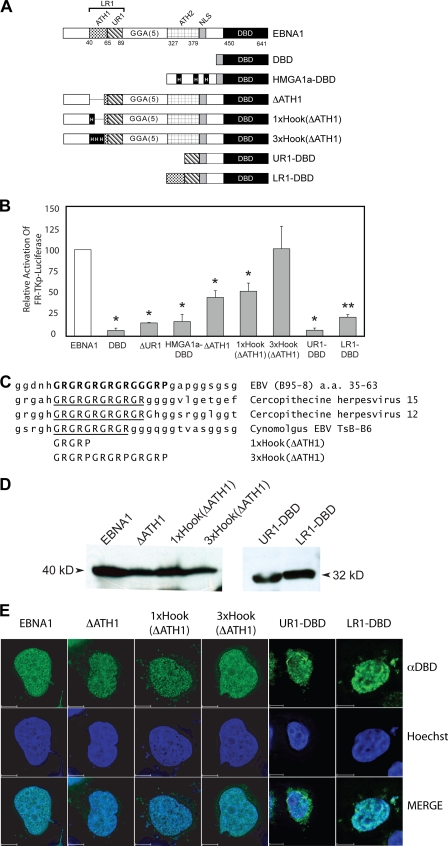
FIG. 5.
EBNA1's AT-hook domains significantly augment transactivation of an integrated FR-TK-luciferase reporter in BJAB cells. (A) A schematic depiction of wild-type EBNA1 and EBNA1 derivatives expressed in BJAB/FR-TK-luciferase cells. The DBD contains a fusion to EBNA1's nuclear localization signal (NLS) to aa 450 to 641. In ΔUR1, aa 71 to 88 are deleted. HMGA1a-DBD is a fusion of the architectural transcription factor HMGA1a to DBD. The three AT-hooks within HMGA1a are boxed and indicated by a capital H. In ΔATH1, the GR repeat in LR1 from aa 40 to 54 is deleted. The sequence deleted in ΔATH1 is replaced by a single AT-hook from HMGA1a in 1×Hook(ΔATH1) or three copies of this AT-hook in 3×Hook(ΔATH1). UR1-DBD contains a fusion of aa 59 to 89 of EBNA1 to aa 379 to 641. LR1-DBD contains a fusion of aa 40 to 89 of EBNA1 to aa 379 to 641. (B) Expression plasmids for the proteins described above were electroporated into BJAB/FR-TK-luciferase cells along with a cytomegalovirus-EGFP expression plasmid, as described in Materials and Methods. Luciferase activity in extracts was measured 48 h posttransfection and corrected for transfection efficiency, which ranged from 20% to 40%. Wild-type EBNA1 transactivated the reporter approximately 15-fold over the DBD alone, and this value was normalized to 100%. The relative induction observed with the EBNA1 derivatives is expressed as a fraction of 100%. Transactivation that differed significantly from that observed with wild-type EBNA1 (P < 0.05) is indicated by the asterisk. ΔATH1 and 1×Hook(ΔATH1) were similarly impaired in their transactivation of this reporter. In contrast, transactivation by 3×Hook(ΔATH1) could not be distinguished from wild-type EBNA1. (C) Sequence alignment of the GR repeat in LR1 aligned with the corresponding sequence from the indicated EBNA1 orthologs. The substituted sequences in the 3×Hook(ΔATH1) and 3×Hook(ΔATH1) are shown aligned to the GR repeat of the EBNA1 proteins. (D) Expression of EBNA1, ΔATH1, 1×Hook(ΔATH1), 3×Hook(ΔATH1), UR1-DBD, and LR1-DBD in electroporated BJAB/FR-Tk-luciferase cells. Protein from 5 × 105 electroporated cells was detected and visualized as described in Materials and Methods. Standards of known molecular sizes are indicated adjacent to the arrowheads. (E) Expression of EBNA1, ΔATH1, 1×Hook(ΔATH1), 3×Hook(ΔATH1), UR1-DBD, and LR1-DBD in C33a cells evaluated by indirect immunofluorescence. Transfected cells were grown on coverslips and processed for indirect immunofluorescence as described in Materials and Methods. The anti-DBD (αDBD) antibody was visualized with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G, and nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. Staining by the anti-DBD and Hoechst stain is indicated in the merged image of the two. At least 15 z-sections of 200 nm were deconvolved for each image. The scale bar represents a distance of 5 μm.