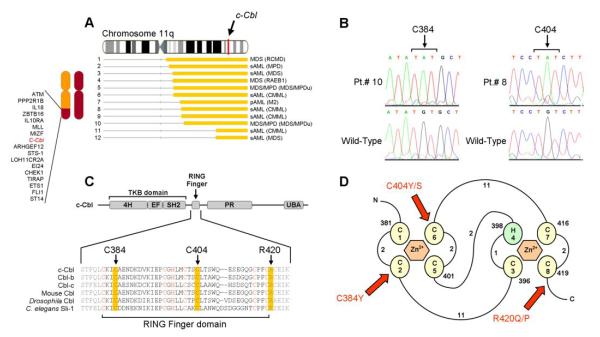
Figure 4. Identification of unique, missense mutations in c-Cbl (11q23.3).
(A) Map of individual UPD lesions on chromosome 11q and the location of the c-Cbl gene. (B) Direct genomic DNA sequencing of exon 8 in c-Cbl reveals the presence of missense mutations. Each base pair change occurs in a homozygous state due to the copy-neutral LOH and results in the substitution of cysteine residues for tyrosine or serine residues at positions 384 (in patients 9 and 10) and 404 (in patients 6, 8, and 12). (C) Schematic representation showing the major domains of mammalian c-Cbl, primarily the tyrosine kinase binding (TKB) domain, RING finger, proline-rich (PR) region, and ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA). Also shown is the amino acid sequence spanning the RING finger domain of mammalian c-Cbl along with homologs Cbl-b, Cbl-c, and those found in Mus musculus, Drosophila, and C. elegans (Sli-1). Critical cysteine/histidine residues that make up the RING finger domain are indicated in red. Residues affected by mutations are highlighted in yellow. (D) Schematic of the prototypical RING finger domain found in c-Cbl (adapted from (39) (Fig1)) C’s denote cysteine residues; H, histidine residues and are numbered in the order with which they occur in the domain. Curved lines represent amino acid chains and are accompanied by numbers which denote their lengths. Red arrows indicate the affected residues in patients positive for the mutations and are accompanied by the resulting amino acid substitutions.