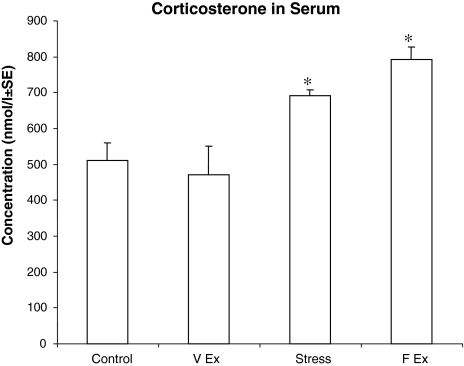
Fig. 1.
Relative levels of corticosterone measured in serum following different treatment regimens. Treadmill exercise showed a significant (* P < 0.05) increase in corticosterone levels as compared to controls, while voluntary exercise showed no significant difference. The shock treatment also led to a significant (* P < 0.05) elevation of corticosterone in comparison to controls (F forced, V voluntary, EX exercise)