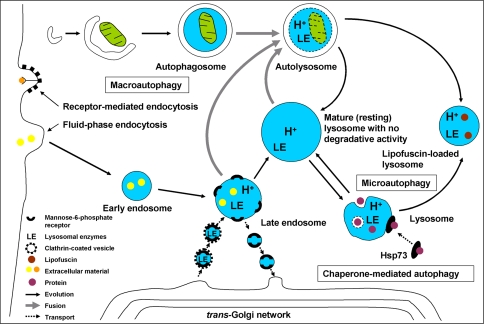
Fig. 1.
Autophagy can be subdivided into three forms: macro-, micro- and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). In macroautophagy, a cup-formed phagophore surrounds cytosolic organelles thereby creating an autophagosome, which fuses with a lysosome or a late endosome. Small portions of cytoplasm enter lysosomes through invagination of the membrane (microautophagy). In CMA, proteins tagged with the amino acid sequence KFERQ are bound by molecular chaperones, e.g., Hsp73, and transported to lysosomes. The latter form from late endosomes from which they differ in that they do not have mannose-6-phosphate receptors (MPR). Lysosomal hydrolases are transported bound to MPRs in Golgi-derived vesicles to slightly acidified late endosomes and, possibly, autophagosomes. There, the enzymes are released and the MPRs are recycled back to the Golgi network