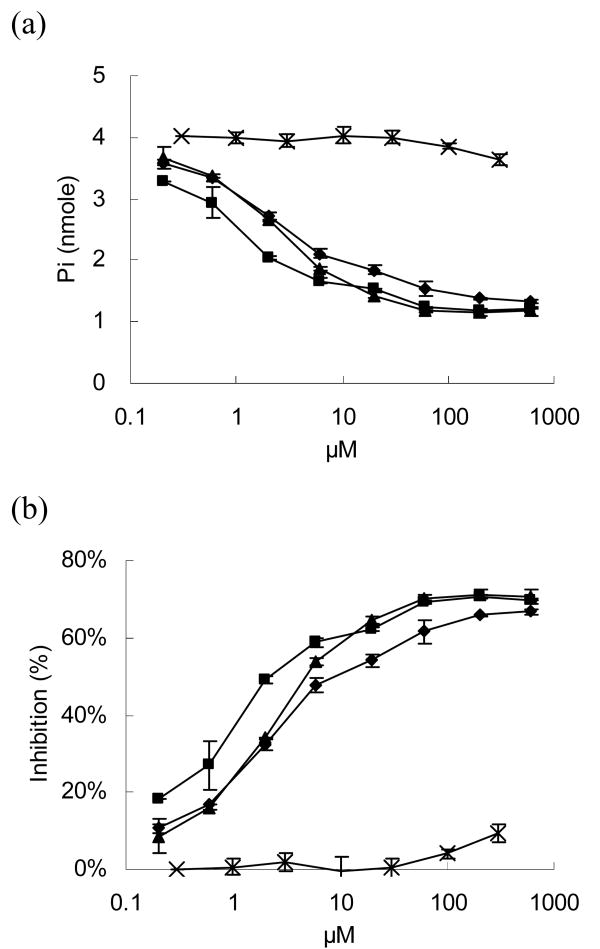
Figure 2.
An ATPase inhibition assay was performed to investigate the potential toxicity caused by DIG modification. ATPase was reacted with different concentrations of DIG-AdLacZ (cross), and the enzymatic activities of ATPase were determined by the freeing of phosphate ions released from ATP. Three different cardiac glycosides, ouabain (triangle), digoxigenin (square), and digoxin (diamond), were compared as positive controls. (a) The phosphate ion concentrations decreased with increasing inhibitors because the enzymatic activity of ATPase was blocked. DIG-AdLacZ only slightly reduced phosphate release. (b) Three cardiac glycoside molecules demonstrated a dose dependent inhibition of ATPase activity, while an equivalent dose of DIG-AdLacZ exhibited nearly undetectable levels.