Figure 2. The impact of measures changing the infectivity of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV).
The transmission probability of chronic HBV from individuals with single HBV infection (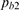 ) was varied from 0 to 0.4. A, B: hepatitis D reduces HBV infectivity by 50% in individuals dually infected (
) was varied from 0 to 0.4. A, B: hepatitis D reduces HBV infectivity by 50% in individuals dually infected (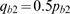 ); C, D: hepatitis D does not suppress HBV replication (
); C, D: hepatitis D does not suppress HBV replication (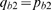 ). Left panels show the total prevalence of HBV (black solid line), the prevalence of hepatitis D (black dashed line), and the prevalence of HBV in a population without hepatitis D (grey line). Right panels show the reproduction numbers Rb (solid line), Rbd (dashed line), and
). Left panels show the total prevalence of HBV (black solid line), the prevalence of hepatitis D (black dashed line), and the prevalence of HBV in a population without hepatitis D (grey line). Right panels show the reproduction numbers Rb (solid line), Rbd (dashed line), and 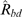 (dotted line).
(dotted line).

