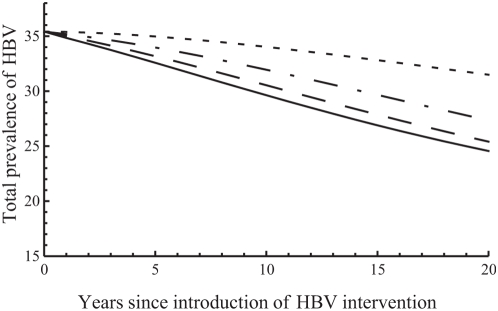
Figure 6. The initial impact of treatment on the prevalence of hepatitis B (HBV).
Antiviral treatment reduces infectivity of chronic HBV by 20%. The total prevalence of HBV is shown as percentage of the population. When the intervention is introduced (year 0), 36% of the population is infected with HBV; among them, the percentage coinfected with hepatitis D is 30% (solid line), 20% (dashed line), 10% (dashed-dotted line), or 0% (dotted line).