Table 1. Parameter definitions and values.
| Symbol | Definition | Value | Source* |

|
Progression rate from acute to carrier for HBV | 0.4/person/year | [27]–[29] |
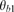
|
Recovery rate from acute infection with HBV | 3.6/person/year | [27]–[29] |
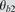
|
Recovery rate from chronic infection with HBV | 0.02/person/year | [25], [28] |

|
Transmission risk of HBV from person with HBV only, stage 1 | 0.46 | [25], [30] |
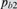
|
Transmission risk of HBV from person with HBV only, stage 2 | 0.65 
|
[25], [30] |
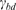
|
Progression rate from acute to carrier for those dually infected | 2/person/year | [2], [28], [31] |
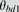
|
Recovery rate from acute infection for those dually infected | 2/person/year | [2], [28], [31] |
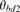
|
Recovery rate from chronic infection for those dually infected | 0.02/person/year | [25], [28] |
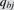
|
Transmission risk of HBV from person with dual infection, stage j = 1, 2 | 0.71 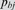
|
[6] |
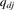
|
Transmission risk of hepatitis D from person with dual infection, stage j = 1, 2 |
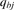
|
|
| n | Initial total population size | 26000 | [32] |
| μ | Rate of departing from the population | 0.018/year | |
| B | Rate at which individuals enter the uninfected population | μn | |
| ϕ | Rate of partner change | 1.64 partners/year | [33], [34] |
HBV, hepatitis B virus. Dually infected are individuals infected with both hepatitis B and hepatitis D viruses. The transmission risks are expressed as probabilities of transmission per partnership. The stages 1 and 2 of infection (single HBV and dual) are the acute and the chronic stages, respectively.
See details in the Supporting Information, text S1.
