Figure 1. Auranofin inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB and IRF3 activation.
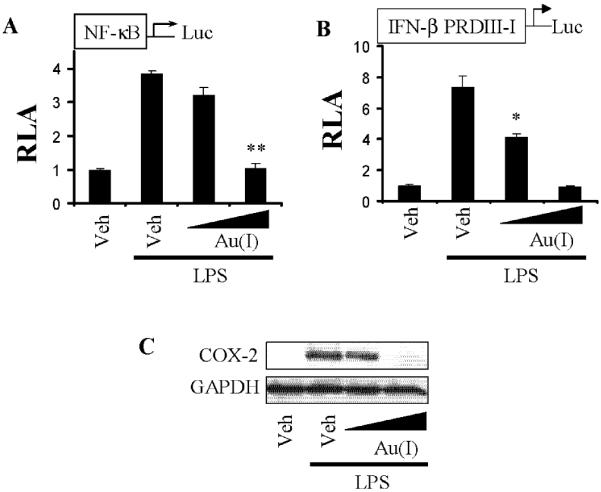
A,B) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with (A) NF-κB or (B) IFNβ promoter with specific IRF3 binding site (IFNβ PRDIII-I) luciferase reporter plasmid and pre-treated with auranofin (5, 10 μmM) for 1 h, and then treated with LPS (5 ng/ml) for an additional 6 hrs. Cell lysates were prepared and luciferase and β-galactosidase enzyme activities were measured as described in “Materials and Methods”. Relative luciferase activity (RLA) was normalized with β-galactosidase activity. Values are mean±SEM (n=3). *, Significantly different from LPS alone, p<0.05. **, Significantly different from LPS alone, p<0.01. C) RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with auranofin (5, 10 μM) for 1 hr and then further stimulated with LPS (5 ng/ml) for 6 hrs. Cell lysates were analyzed for COX-2 and GAPDH protein by immunoblots. The panels are representative data from more than three independent experiments. Veh, vehicle; Au(I), auranofin.
