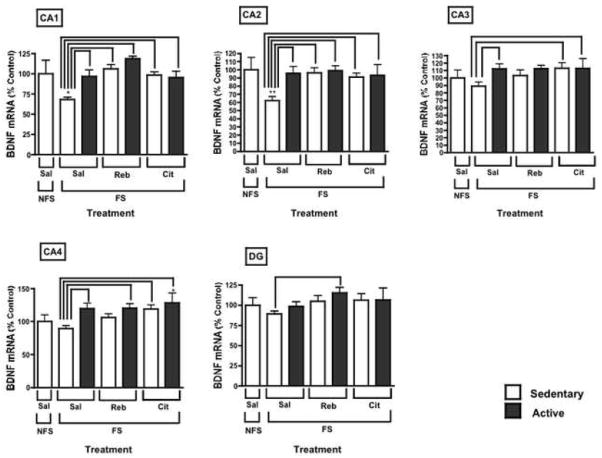
Fig. 2.
Forced swimming decreased BDNF mRNA levels in the CA1 and CA2; this effect was prevented with all interventions tested. Several interventions also significantly increased BDNF mRNA relative to FS levels in the remaining hippocampal regions. Results are displayed as the percentage of control (Saline/Sedentary/No forced swim) and represent the mean ± S.E.M. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences from control group (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Bridges between bars denote statistical significance between the indicated groups (p < 0.05). All treatments were administered for an acute period of 1 week (NFS: no forced swim; FS: forced swim; Sal: saline; Reb: reboxetine; Cit: citalopram; Sedentary: no access to running wheel; Active: voluntary access to running wheel).