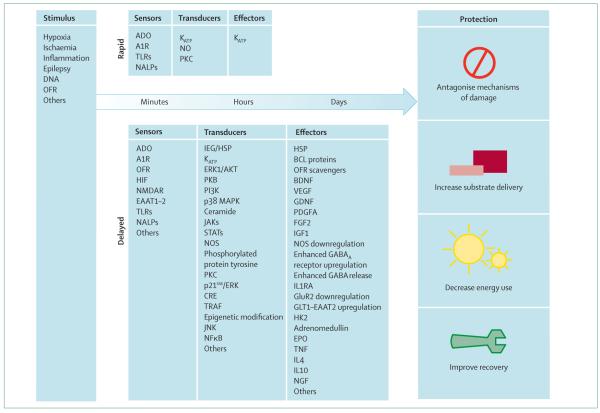
Figure 2. Signalling cascades of preconditioning.
Various stimuli lead to protection via modules of sensors, transducers, and effectors. Adapted from Dirnagl et al,4 with permission from Elsevier. A1R=adenosine receptor type 1. ADO=adenosine. Akt=a serine/threonine kinase family. BDNF=brain-derived neurotrophic factor. CRE=cyclic AMP response element. EAAT=excitatory amino-acid transporter. EPO=erythropoeitin. ERK=extracellular signal-regulated kinase. FGF2=fibroblast growth factor 2. GDNF=glia-derived growth factor. GluR2=glutamate receptor subunit 2. GLT=glutamate transporter. HIF=hypoxia-inducible factor. HK2=hexokinase 2. HSP=heat shock protein. IEG=immediate early gene. IGF1=insulin-like growth factor 1. IL=interleukin. IL1RA=interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. JAK=janus kinase. JNK=c-Jun N-terminal kinase. KATP=ATP-sensitive potassium channel. MAPK=mitogen-activated protein kinase. NALP=NACHT-containing, LRR-containing, and pyrin-domain-containing protein. NFκB=nuclear factor κB. NGF=nerve growth factor. NMDAR=NMDA receptor. NO=nitric oxide. NOS= nitric oxide synthase. OFR=oxygen free radicals. PDGFA=platelet-derived growth factor receptor A. PI3K=phosphoinositide-3 kinase. PKB=protein kinase B. PKC=protein kinase C. STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription.TNF=tumour necrosis factor. TLR=Toll-like receptor. TRAF=TNF receptor-associated factor. VEGF=vascular endothelial growth factor.