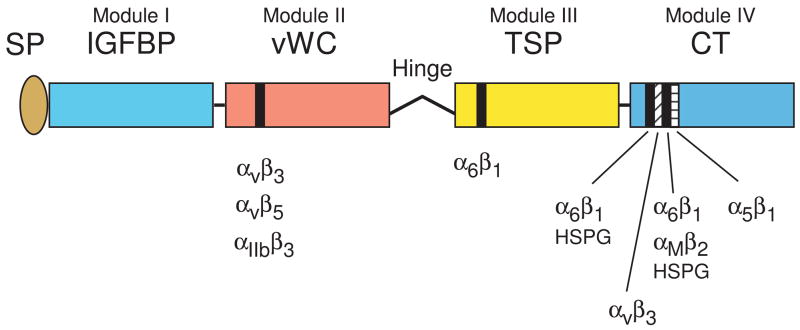
Figure 1.
Schematics of CCN protein structure and localization of their integrin binding sites. The six CCN proteins include CCN1 (CYR61), CCN2 (CTGF), CCN3 (NOV), CCN4 (WISP-1, ELM1), CCN5 (WISP-2, COP-1), and CCN6 (WISP-3). They share significant structural homology, including an N-terminal secretory signal peptide (SP), followed by modular domains (illustrated in different colors) with sequence homologies to insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP, module I), von Willebrand factor type C repeat (vWC, module II), thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSP, module III), and a cysteine knot containing carboxyl domain (CT, module IV). Throughout the four modules are 38 cysteine residues that are highly conserved. CCN5 uniquely lacks the CT domain but conserves domains I–III. A protease-sensitive hinge region with no sequence homology among the CCN proteins separate domains II and III. Specific binding sites (black and hatched bars) for several integrins and HSPGs have been identified for CCN1 and CCN2 (Chen et al., 2000; Leu et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2004a; Leu et al., 2004; Gao and Brigstock, 2004; Gao and Brigstock, 2006).