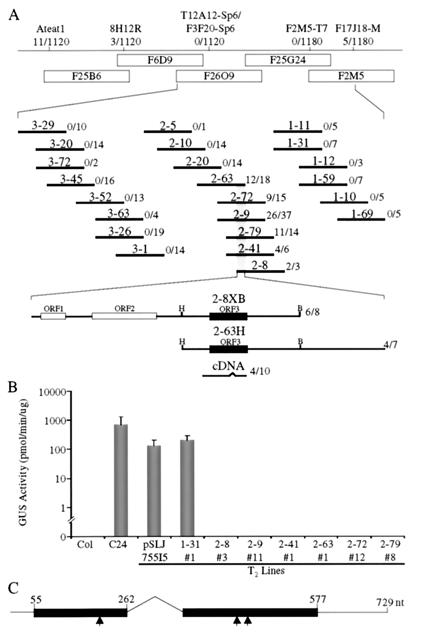
Figure 1.
Cloning of RTM1. (A) PCR-based markers that flank or cosegregate with RTM1 are indicated at the top. The number of recombination events per total number of meiotic events scored is given below each marker. A BAC contig spanning RTM1 is shown (open boxes). Cosmids (solid lines) derived from BACs F2M5 (cosmids with prefix 1), F25G24 (prefix 2), and F26O9 (prefix 3) were introduced into Arabidopsis ecotype C24 (rtm1/rtrm1). The complementing interval is shaded. Putative ORFs are indicated by boxes in the bottom expanded region. The HindIII (H) and BsaAI (B) restriction sites used to generate 2–63H and 2–8XB, respectively, are indicated. The number of putative C24 transformants that restricted long-distance movement of TEV-GUS per total plants tested is shown adjacent to each clone. (B) GUS activity assays of selected TEV-GUS-infected T2 C24 lines containing complementing cosmids (2–8 #3, 2–9 #11, 2–41 #1, 2–63 #1, 2–72 #12, 2–79 #8), a noncomplementing cosmid (1–31 #1), or empty vector (pSLJ755I5), or wild-type susceptible (C24) and nonsusceptible (Col-0) lines. Inflorescence tissue from 10 T2 individuals was tested at 20 days postinoculation. The mean GUS activity value (+ SD) is shown. (C) Representation of the RTM1 cDNA, with the nucleotide positions of the start codon (nucleotide 55), 5′ intron splice site (nucleotide 262), stop codon (nucleotide 577), and 3′ terminal nucleotide (nucleotide 729) indicated. Arrows indicate positions of amino acid substitutions in rtm1 mutant alleles.