Figure 1. Hematopoietic reconstitution potential and homing activity of junB-deficient bone marrow cells.
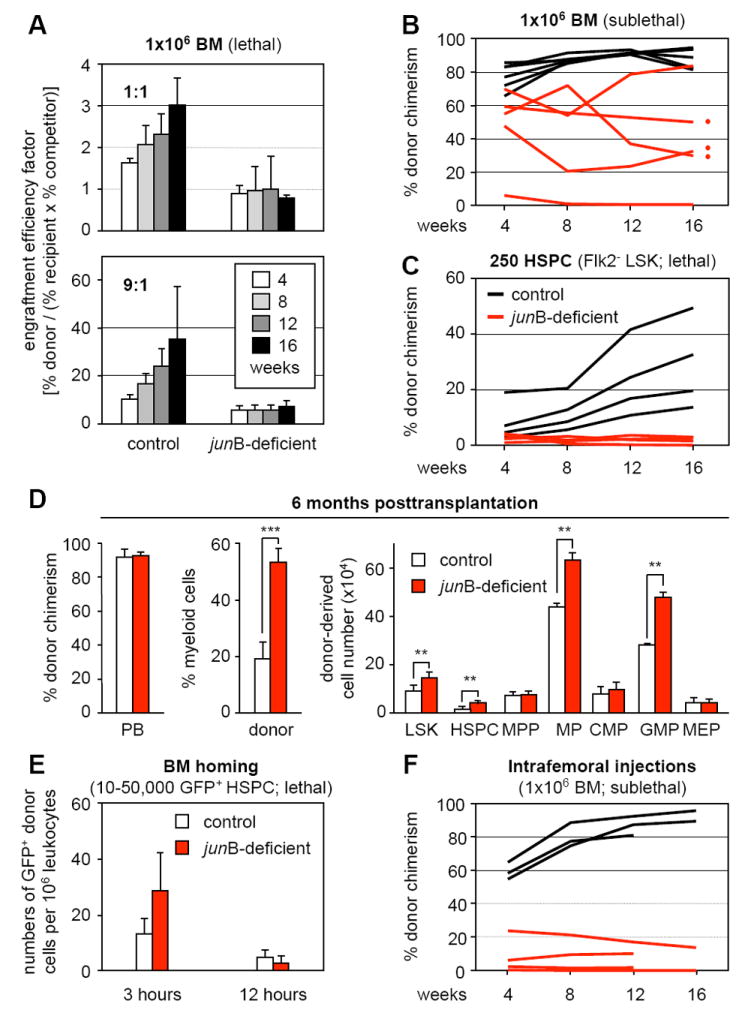
Lethally or sublethally irradiated recipients (CD45.1) were transplanted with the indicated numbers and type of donor control or junB-deficient cells (CD45.2). Mice were bled every 4 weeks and analyzed for % CD45.2 chimerism in PB.
(A) Transplantation of 1×106 unfractionated BM cells (1:1 and 9:1 ratio of donor and competitor GFP+/CD45.1 cells) into lethally irradiated recipients (n = 5 mice per cohort). Engraftment efficiency factor (percentages ± SD) was calculated as [(% CD45.2+ donor cells)/((% CD45.1+ recipient and competitor cells) × (% GFP+ competitor cells))].
(B) Transplantation of 1×106 unfractionated BM cells into sublethally irradiated recipients (n = 5 mice per cohort).
(C) Transplantation of 250 purified HSPCs (Flk2- KLS) together with 3×105 helper CD45.1 BM cells into lethally irradiated recipients (n = 4 mice per cohort).
(D) MPD development in recipients of junB-deficient BM cells (red dots in panel B). The % CD45.2 chimerism and donor-derived myeloid (Gr-1+/Mac-1+) cells in PB, and the total cell numbers for the indicated BM subpopulations is given at 6 months posttransplantation (averages ± SD; n = 3 mice per cohort; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001). MPP: multipotent progenitors (Flk2+ LSK); MP: myeloid progenitors (Lin-/Sca-1-/c-Kit+); CMP: common myeloid progenitors; GMP: granulocyte/macrophage progenitors; MEP: megakaryocyte/erythrocyte progenitors.
(E) Short-term in vivo homing assay. Sublethally irradiated recipients (n = 3 mice per cohort) were injected with either 50,000 LSK (3 hours) or 10,000 Flk2- LSK (12 hours) cells isolated from β-actin GFP control and junB-deficient mice. The number (averages ± SD) of transplanted GFP+ cells present in the BM was determined at 3 or 12 hours postinjection.
(F) Intrafemoral injections. Unfractionated 1×106 BM cells were directly injected into the femoral cavity of sublethally irradiated recipients (1 femur injected per mouse, n = 3 to 4 mice per cohort).
