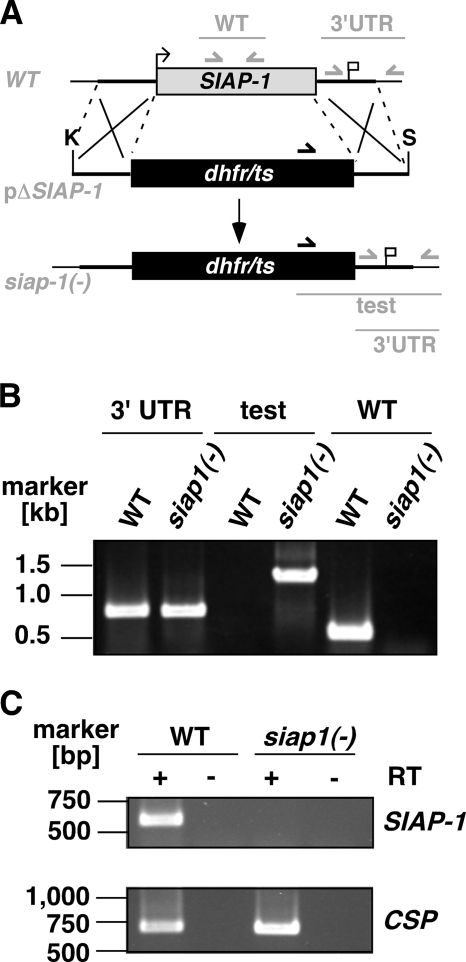
FIG. 3.
Targeted deletion of the P. berghei SIAP-1 gene. (A) Replacement strategy for targeted gene disruption of PbSIAP-1. The WT SIAP-1 locus (WT) is targeted with a KpnI (K)/SpeI (S)-linearized replacement plasmid (pΔSIAP-1) containing the 5′ and 3′ UTR of PbSIAP-1 and the positive selection marker TgDHFR-TS. After double-crossover homologous recombination, the SIAP-1 ORF is substituted by the selection marker, resulting in the mutant siap-1(−) allele. Replacement- and WT-specific test primer combinations and expected fragments are shown as lines. (B) Replacement-specific PCR analysis. Confirmation of the predicted gene targeting is done with primer combinations that amplify only a signal in the recombinant locus (test). The absence of a WT-specific signal in the clonal siap-1(−) parasite population confirms the purity of the mutant parasite line. (C) Depletion of SIAP-1 transcripts in siap-1(−) parasites. cDNA from WT and siap-1(−) sporozoites were used as a template for SIAP-1-specific PCRs (top). Amplification of the circumsporozoite protein (CSP) transcripts was used as a positive control (bottom).