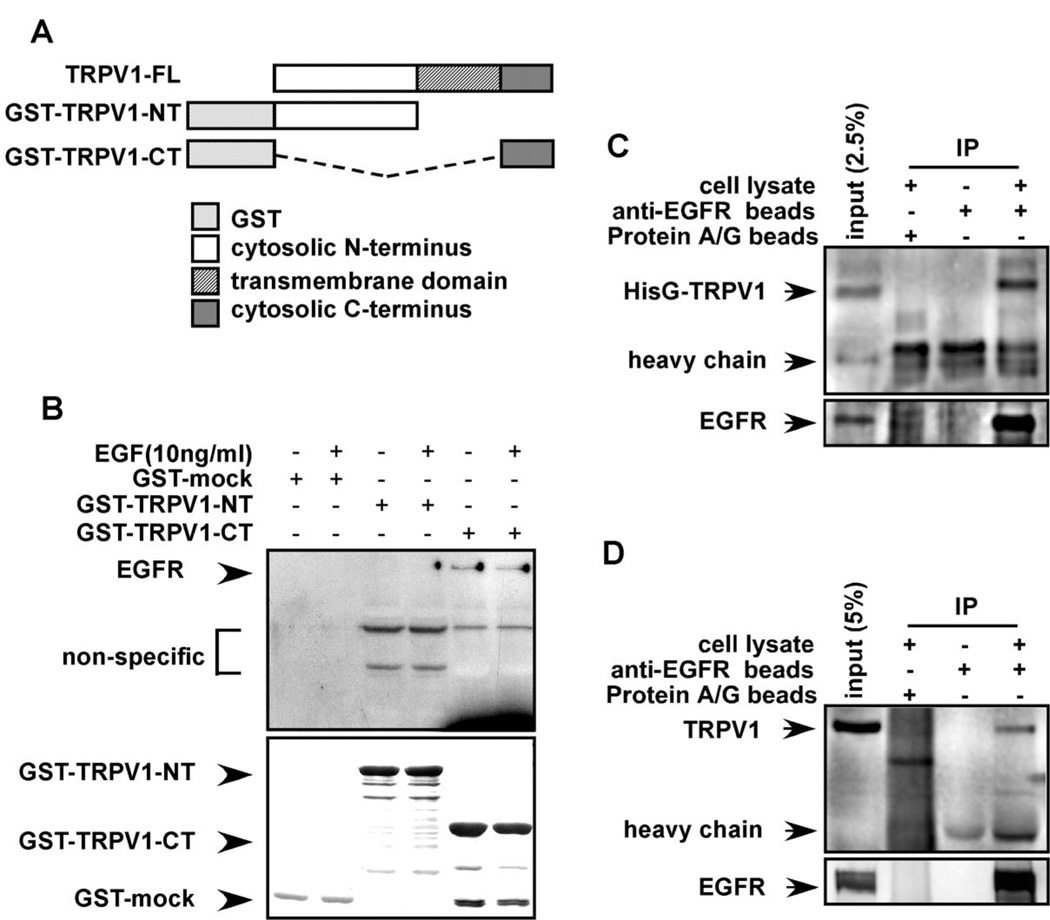
Figure 2.
The TRPV1 and EGFR interact in vitro and ex vivo. (A) GST-fusion protein constructs were created as follows: TRPV1-FL (full length TRPV1); GST-TRPV1-NT (N-terminal cytoplasmic domain of TRPV1); and GST-TRPV1-CT (C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of TRPV1). (B) The EGFR binds to the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of the TRPV1. The GST-mock, GST-TRPV1-NT, or GST-TRPV1-CT protein was mixed with membrane fractions from A431 human skin cells and incubated overnight. Anti-EGFR was used to detect binding of the EGFR to respective GST-TRPV1 proteins. The top panel illustrates the binding interaction and the bottom panel verifies input. (C) The membrane proteins from HEK293 cells transfected with pcDNA4-HisG-TRPV1 were immunoprecipitated with beads pre-conjugated with anti-EGFR and the co-immunoprecipitated TRPV1 was visualized by Western blotting with anti-HisG. (D) The membrane proteins from HaCaT cells were immunoprecipitated with beads pre-conjugated with anti-EGFR and the co-immunoprecipitated TRPV1 was visualized by Western blotting with anti-TRPV1. For C and D, immunoprecipitated EGFR is shown in the lower panel.