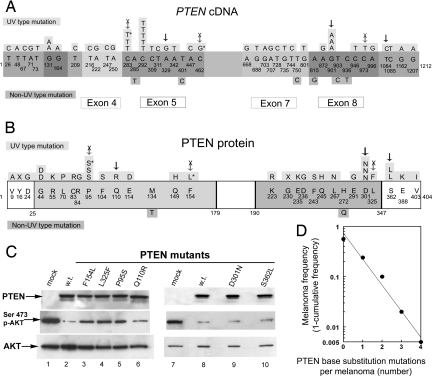
Fig. 2.
Location of PTEN mutations in melanomas and effect of mutations on PTEN function. (A) Sites of 52 PTEN cDNA base substitution mutations found in 33 melanomas from 8 XP patients. The 9 exons of the 1212 bp PTEN cDNA are indicated. Mutated bases are numbered. UV type mutations are indicated above the exons and non-UV type mutations are indicated below the exons. An * indicates cancer-associated mutation listed in the Sanger COSMIC database (22). Vertical arrows indicate mutations tested for alteration of PTEN function. Arrows with X indicate mutations that result in decreased PTEN function. (B) Sites of 33 PTEN nonsynonymous amino acid substitution mutations and 2 nonsense mutations found in 33 melanomas from 8 XP patients. The 404 aa protein has a dual specificity protein phosphatase domain from amino acid 25 to 179, a tyrosine specific protein phosphatase region from amino acid 123 to 134 and a C2 calcium/lipid-binding region, (CaLB) from amino acid 190 to 347. The altered amino acids are numbered. UV type mutations are indicated above the sequence and non-UV type mutations are indicated below. An * indicates cancer associated mutation listed in Sanger COSMIC database (22). Vertical arrows indicate mutations tested for alteration of PTEN function. Arrows with X indicate mutations that result in decreased PTEN function. (C) Functional assay of phosphorylation of Akt by selected PTEN mutants. NCI-H1155 PTEN-null cells were transfected with pCMV5 HA-PKB/Akt (containing hemagglutinin (HA) tagged PKB/Akt) plus pCMV5 with wild type (w.t.) (lanes 2 and 8) or mutated (lanes 3–6, 9–10) PTEN or empty vector (mock) (lanes 1 and 7). After 24 h, the cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies. This HA-PKB/Akt was analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-Akt phosphoserine 473 antibody (Middle). The membrane was then stripped and analyzed using an antibody against total Akt (Lower). Expression of transfected PTEN proteins was confirmed by anti-PTEN Western blot analysis of cell lysates (Upper). The phosphorylation of Akt by mutants p.F154L (lane 3), p.L325F (lane 4), and p.P95S (lane 5) indicates loss of PTEN suppressor function while the low level of phosphorylation of Akt by mutants p.Q110R (lane 6), p.D301N (lane 9), and p.S362L (lane 10) indicates preservation of PTEN suppressor function. (D) Relationship of number of PTEN base substitution mutations per melanoma to melanoma frequency (1- cumulative frequency). The data are consistent with a random (Poisson) distribution of mutations.