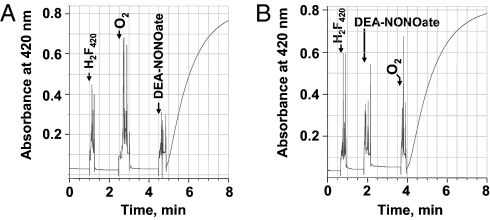
Fig. 2.
Oxidation of F420H2 by nitric oxide in the presence of oxygen. Nitric oxide was generated in situ from NONOate derivatives. Into a 1-mL anaerobic solution of 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) in a stoppered cuvette with N2 in the headspace, the following were added to the final concentrations and in the sequence indicated: (A) Reduced F420 (20 μM), oxygen (80 μM), and DEA-NONOate (320 μM). (B) Reduced F420 or F420H2 (20 μM), DEA-NONOate (320 μM), and oxygen (80 μM). The time of each addition is shown by an arrow. Oxidation of F420H2 was monitored spectrophotometrically at 420 nm. DEA-NONOate, 2-(N,N-diethylamino)-diazenolate-2-oxide sodium salt; DETA-NONOate, 2,2′-(hydroxynitrosohydrazino)bisethanamine; spermine-NONOate, N-[4-[1-(3-aminopropyl)-2-hydroxy-2-nitrosohydrazino]butyl]-1,3-propanediamine.