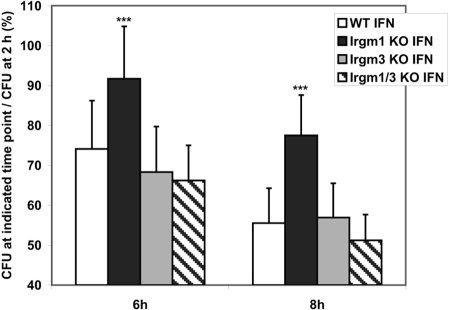
Fig. 2.
Normal IFN-γ-induced suppression of S. typhimurium in Irgm1/3 KO macrophages. BMM of the indicated genotypes were cultured for 24 h under control conditions or in the presence of 100 U/ml IFN-γ, as indicated. The cells were subsequently infected with S. typhimurium SL1344 at a moi of 2:1. At 2, 6, and 8 h postinfection in medium containing gentamycin to inhibit extracellular bacterial growth, CFUs were determined from triplicate samples. Shown are the composite results from five experiments. To illustrate the effect on intracellular bacterial survival, the data are displayed as the ratio of the CFU remaining at 6 and 8 h to the CFU present at the initial 2-h time-point. The error bars indicate sd; ***, statistically significant differences relative to WT levels at that time-point (P<0.05). In IFN-γ-activated cells, the differences between values in WT and Irgm1 KO BMM were statistically significant at 6 and 8 h (P=0.012 and 0.0048, respectively), and none of the differences between WT and Irgm3 KO BMM or WT and Irgm1/3 KO BMM were significant. In BMM cultured under control conditions, none of the data for the Irgm1 KO, Irgm3 KO, or Irgm1/3 KO BMM was statistically different from those in the WT BMM at 6 or 8 h.