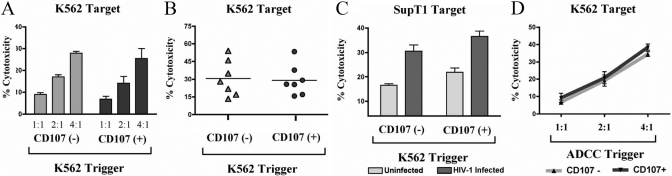
Fig. 3.
Cytolytic capacity of CD107+ and CD107– sorted NK cells. (A) Purified NK cells were incubated with K562 target cells for 3 h at a 4:1 E:T ratio and sorted as in Figure 1A. CD107– and CD107+ sorted NK cells were then incubated with chromium-labeled K562 cells at multiple E:T cell ratios for 3 h, and a fraction of the supernatant was collected and tested in a γ-scintillation counter. Percentage cytotoxicity was calculated as described previously [16]. (B) Purified NK cells from seven individual donors were incubated with K562 target cells for 3 h at a 4:1 E:T ratio and sorted as in Figure 1A. CD107– and CD107+ sorted NK cells were then incubated with chromium-labeled K562 cells at a 4:1 E:T ratio for 3 h in a standard chromium lysis assay. (C) Purified NK cells were incubated with K562 target cells for 3 h at a 4:1 E:T ratio and sorted as in Figure 1A. CD107+ and CD107– sorted NK cells were then incubated with chromium-labeled, HIV-1-infected or -uninfected SupT1 cells at a 4:1 E:T ratio for 3 h. To generate HIV-1-infected SupT1 targets, SupT1 cells were infected with 150 ng HIV-1 × 4 tropic primary isolate (r) (TYBE) containing supernatant and centrifuged for 2 h at 1800 rpm in the presence of 8 μg/ml polybrene. HIV-1-infected SupT1 cells were incubated for 4 days until they were 95% p24-positive and then used as targets in chromium lysis assay. (D) Purified NK cells were incubated with antibody-coated CEM×174 targets for 3 h at a 4:1 E:T ratio and sorted as in Figure 1 A. CEM×174 cells were coated with 1 mg HIV-1 gp120 and incubated with a 1/1000 dilution of HIV-1-infected subject sera to induce ADCC. CD107+ (dark gray bar)- and CD107– (light gray bar)-sorted NK cells were then incubated with chromium-labeled K562 cells at a 4:1 E:T ratio for 3 h in a standard chromium cytotoxicity assay. Error bars represent the sd of the mean of quadruplicate values from each representative experiment.