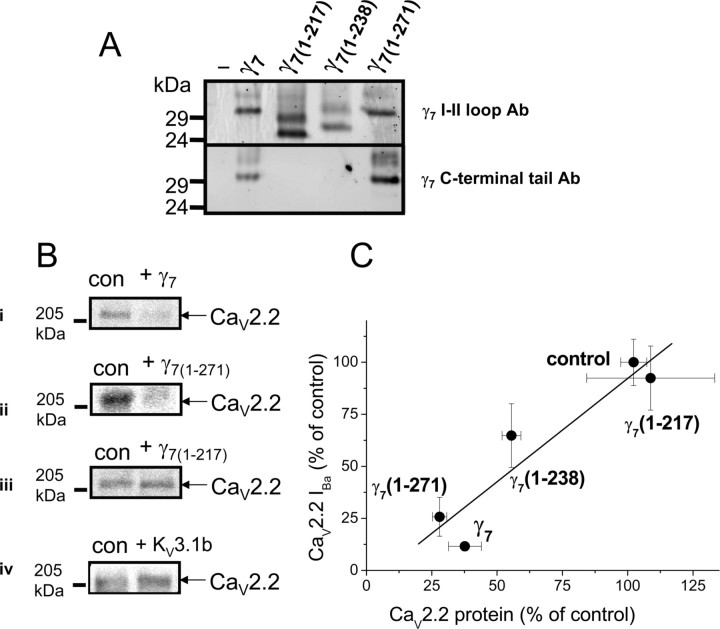
Figure 2.
Effect of C-terminal truncation of γ7 on CaV2.2 protein. A, γ7 and truncated γ7 constructs were expressed at the expected sizes in COS-7 cells (top, γ7 I–II loop Ab; bottom γ7, C-terminal tail Ab). In each lane, the lower band corresponds to the expected protein molecular weight, and the upper band(s) correspond to either the mature glycosylated form or intermediate glycosylated species. As expected, γ7(1–217) and γ7(1–238) were not detected by the γ7(C-terminal tail) Ab. The specificity of the Abs is indicated by the lack of immunostaining in the absence of transfected constructs (−). Similar results were obtained in Xenopus oocytes (data not shown). The same amount of total protein was loaded in each lane (25 μg). B, Examples of Western blots showing the effect of γ7 (i) and γ7(1–271) (ii) and the lack of effect of γ7(1–217) (iii) and KV3.1b (iv) on the level of CaV2.2 protein expressed in COS-7 cells. con, Transfection with Kir–AAA cDNA, in place of γ7 (see Materials and Methods). The same amount of total protein was loaded in each pair of lanes (25 μg). C, Correlation between the effect of the γ7 and its various C-terminal truncated constructs on the level of CaV2.2 protein with their effect on CaV2.2 I Ba shown in Figure 1 C. The effect of γ7, γ7(1–217), γ7(1–271), and γ7(1–238) on CaV2.2 protein levels represents the mean inhibition observed in 3–10 experiments. The linear fit has a correlation coefficient, r, of 0.936. All error bars are SEM.