Figure 2.
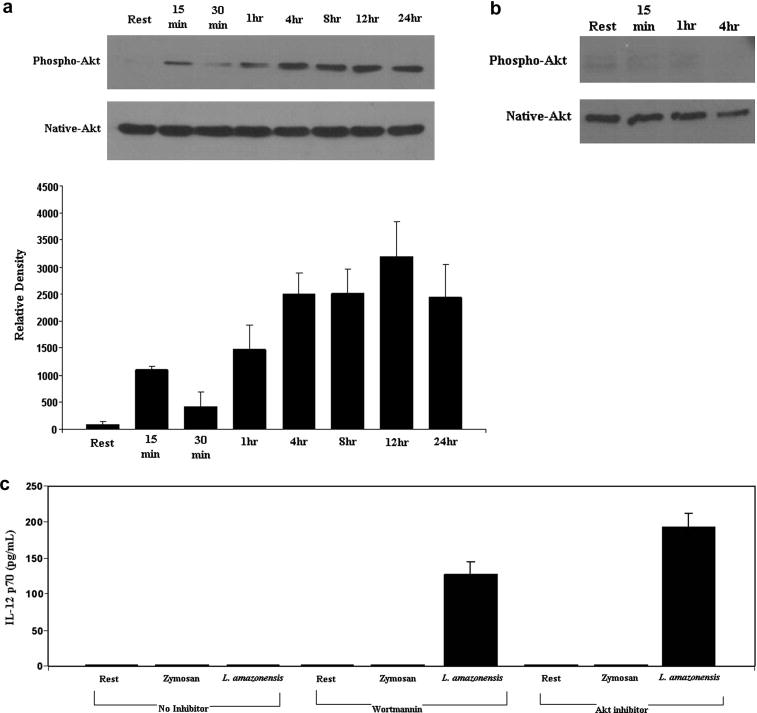
L. amazonensis infection activates PI3K/Akt signaling and inhibition of components in this pathway restores IL-12p70 production in L. amazonensis infected BMDMϕ. A) Macrophage lysates were prepared at the indicated times after infection and then analyzed in Wesern blots for the presence of activated Akt with anti-phospho-Akt (Ser 473). The blots were stripped and re-probed with antibodies to native Akt. Densitometric analysis of blots from several experiments was performed with ImageJ software and results were normalized to native protein levels. B) Akt activation was inhibited when infection was performed in the presence of the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (100nM). Parallel infections were performed with vehicle and infected cells with results similar to the data presented in Figure 2A. C) Supernatant fluid was obtained after 24 hours from macrophage cultures that were incubated with Zymosan or infected with L. amazonensis parasites at an MOI of 10. IL-12p70 concentrations in these culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. Resting cells yielded similar results to vehicle treated resting and vehicle treated infected cells. These data are compiled from three experiments
