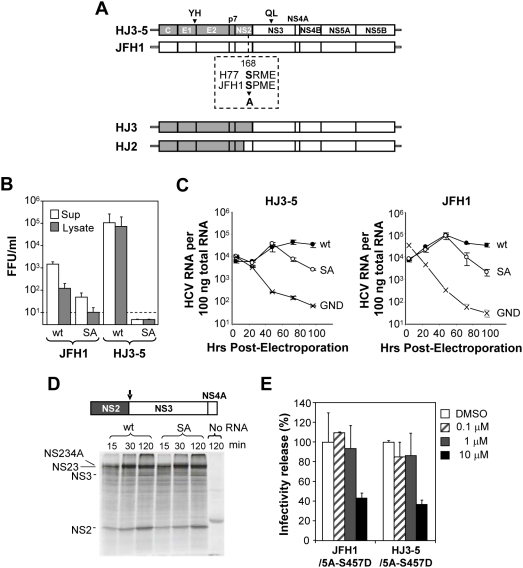
Figure 1. A single mutation in NS2 disrupts infectious virus production without affecting viral RNA replication.
(A) Structure of the chimeric HJ3-5 and JFH1 HCV RNAs. HJ3-5 has two compensatory mutations, located within the E1 (YH) and NS3 (QL) sequences from its HJ3 parent [14]. Also shown is the HJ2 chimera, in which the NS2 protein is itself chimeric. The H77 sequence is represented by the shaded boxes, while the JFH1 sequence is open. The location of the putative CK2 phosphorylation site and the S168A mutation within NS2 is highlighted. (B) Infectious virus titers present in supernatant fluids and cell lysates 2 days following transfection of FT3-7 cells with the JFH1 and HJ3-5 RNAs, with (“SA”) or without (“wt”) the S168A mutation. The limit of detection of infectious virus, determined in a replication focus-forming assay (10 FFU/ml), is indicated by the dashed line. (C) Replication of HJ3-5 (left panel) and JFH1 (right panel) RNAs with or without the SA mutation. “GND” represents a mutant genome defective in RNA replication due to the mutation of GDD to GND within NS5B polymerase active site. Viral RNA abundance was measured by quantitative RT-PCR assay of 100 ng of total RNA derived from cell lysates harvested at 4, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h following transfection of the indicated RNA into FT3-7 cells. The data represent a triplicate analysis, ±S.D. (D) Auto-processing of the NS2-NS3 junction site in NS2-NS3-NS4A polyprotein segments translated in vitro in reticulocyte lysates programmed with wt versus the S168A mutant HJ3-5 RNA. The organization of the proteins translated in vitro are shown at the top. Below are shown the protein products of in vitro translation reactions (15–120 min reaction time), separated by SDS-PAGE. There was no difference in the rate of generation of the mature NS2 protein over time in the presence or absence of the SA mutation. (E) Treatment with sub-toxic concentrations of the CK2 inhibitor DMAT does not reduce virus yields from JFH1 or HJ3-5-transfected cells. In addition to the presence or absence of the NS2 SA mutation, the RNAs transfected in this experiment each contained an S457D mutation in NS5A, which eliminates the need for CK2 phosphorylation of this viral protein. The inhibitor was added to the media from 4 to 24 h post-transfection; virus yields were determined by titration of supernatant fluids collected at 48 h.