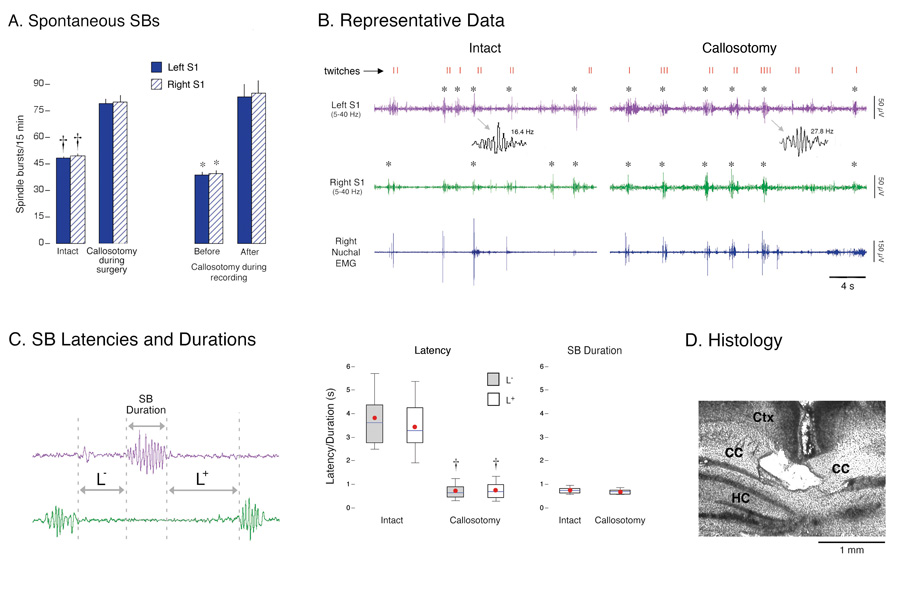
Figure 2. Spontaneous spindle-bursts (SBs) in intact and callosotomized P1–6 rats.
(A) Left: Mean number of spontaneous SBs in left (solid) and right (hatched) S1 during 15-min recording periods. Two procedures were used: pups experienced sham surgery (intact) or callosotomy before recording (n = 6 per group), or pups were callosotomized during the recording session (n = 6). * P < 0.001 in relation to the callosotomy group or post-callosotomy period. Mean + s.e. (B) Representative periods of active sleep in an intact P6 subject and a callosotomized P5 subject. Traces depict right nuchal EMG and right (green) and left (purple) S1 EEG activity (band-pass filter: 5–40 Hz). Behaviorally scored myoclonic twitches of the limbs (red ticks) are also shown and confirmed SBs are denoted by asterisks. Note that SBs in both subjects occur reliably during periods of twitching. Two SBs are expanded to illustrate increased oscillation frequency after callosotomy. S1 activity sometimes increased during periods of twitching but was not categorized as an SB. This is because, upon closer examination, this activity did not exhibit the regular, sinusoidal features characteristic of SBs; instead, this non-SB activity was highly irregular in both frequency and amplitude. (C) Left: Illustration of the method used to measure SB durations and the latencies between SBs in different hemispheres. Right: Box plots depicting distributions of SB latencies and durations for intact and callosotomized subjects (n = 6 per group). The top, middle, and bottom horizontal lines of the box represent the 75th, 50th (median), and 25th percentiles, respectively. The thin vertical lines above and below the box represent the 90th and 10th percentiles, respectively. Red circles are means. † P < 0.0001 in relation to the intact group. (D) Coronal section showing severed corpus callosum (CC) ventral to cerebral cortex (Ctx) and dorsal to hippocampus (HC).