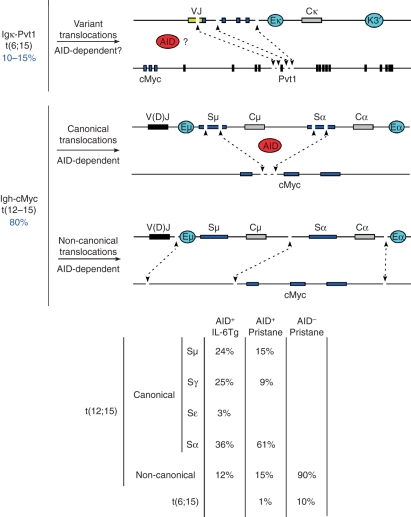
Figure 3.
Classification of chromosomal translocations isolated from mouse plasmacytomas. Upper schematic exemplifies variant translocations [t(6;15)] that juxtapose VJk domains to Pvt1 exon 5. Middle schematic shows activation-induced cytidine deiminase (AID)-mediated deamination during class switch recombination results in the formation of DNA double-strand breaks at S domains and less frequently at cMyc intron 1. Aberrant repair of these lesions can lead to the juxtaposition of cMyc to the immunoglobulin loci. Lower schematic: although at a significantly lesser extent, random, AID-independent DNA breaks can also translocate the cMyc gene to the immunoglobulin loci leading to T(12;15). Translocation breakpoints in these non-canonical translocations often map several kilobases away from S domains or the cMyc gene itself. Right table indicates the percentage of CTs involving diverse S domains in AID+/+ interleukin-6 transgenic mice, and pristane-treated AID+/+ and AID−/− B/c mice.