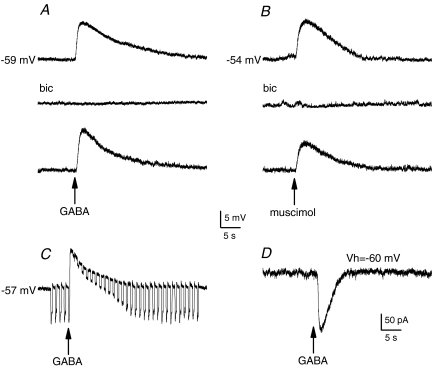
Figure 1. Effects of GABA on membrane potential and ionic currents in isolated petrosal neurones.
A, application of a ‘puff’ of GABA (at arrow; 0.1 mm in pipette) elicited membrane depolarization (upper trace) that was blocked in the presence of the GABAA receptor antagonist (bicuculline (bic); 0.1 mm) in the bath (middle trace), and the effect was reversible (lower trace). B, using the same procedure, muscimol (50 μm), a GABAA receptor agonist, mimicked the effects of GABA (upper and lower traces), and the response was similarly inhibited by bicuculline (middle trace). The depolarization induced by puffer-applied GABA was associated with a conductance increase, as revealed by application of constant hyperpolarizing current pulses (C). Under voltage clamp, a puff of GABA produced an inward current at a holding potential Vh of −60 mV. All recordings were obtained using the gramicidin perforated-patch technique.