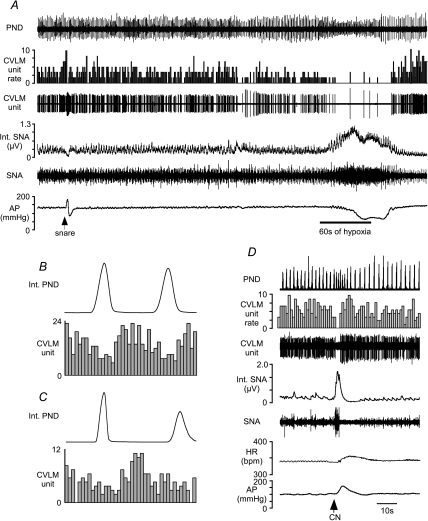
Figure 3. Examples of baro-activated CVLM neurones inhibited by hypoxia.
A, this CVLM neurone was activated by raising AP (snare), but inhalation of hypoxic air (60 s at bar) inhibited the firing of this neurone. B, an AP pulse-triggered histogram shows the pulse-modulated activity of this CVLM neurone. The CVLM unit was counted in 0.01 s bins. C, phrenic-triggered histogram shows a depression of inspiratory-related activity in this CVLM neurone during baseline. The activity of this CVLM unit was counted in 0.1 s bins. D, injection of CN inhibits the firing of this baro-activated CVLM neurone concomitant with increases in SNA and AP. HR, heart rate. bpm, beats · min−1.