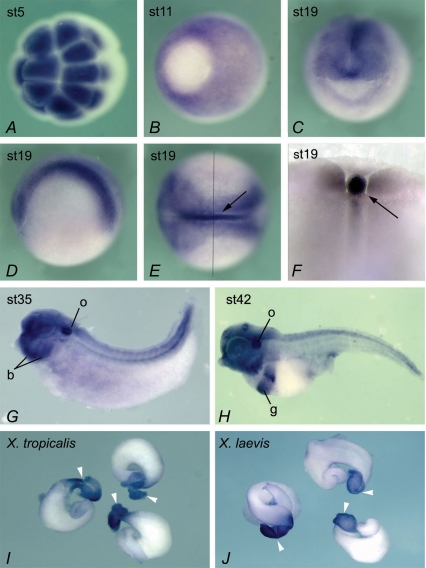
Figure 1. Expression of NKCC1 in Xenopus embryos.
Animal pole view at stage 5, showing high levels of maternal NKCC1 mRNA (A). Vegetal view at gastrula stage 11, with prominent expression in ectoderm. Vegetal pole (embryonic endoderm) shows very little NKCC1 staining (B). Frontal view of stage 19 embryo, showing NKCC1 expression in developing nervous system (C). Lateral view at stage 19, anterior to the left (D). Dorsal view at the same stage, showing high levels of NKCC1 mRNA in neural tissue and the notochord (arrow), and lower level of expression in non-neural ectoderm (E). An embryo in E was dissected along the indicated line, to confirm strong expression of NKCC1 in the notochord and additionally show expression in adjacent somites (F). At tadpole stages 35 in G and 42 in H, NKCC1 continues to be widely expressed, with higher levels of RNA detected in the otic vesicle (o), branchial arches (b) and gut (g). Dorsal is up, and anterior is to the left. Dissected guts at stage 54 from X. tropicalis (I) and X. laevis (J). White arrowheads indicate stomach.